硝化反应在含能材料、医药、农药等生产领域有很广泛的应用。采用硝硫混酸或硝酸-醋酐为硝化剂的传统硝化反应具有硝化系数高、产物后处理流程长、废酸难以回收等缺点,并且不适于水敏和酸敏性物质的硝化。因此,研究者们一直致力于开发一种高效率、零污染的硝化剂,以克服传统硝化反应的缺点。其中,最具发展前景的是五氧化二氮(N2O5)。采用N2O5不仅可实现绿色硝化,而且具有反应温度易控、过程安全;目的产物收率高、产品易分离;可合成传统硝化剂不能制备的一些含能材料等优点[1]。目前,N2O5合成工艺的研究开发已成为硝化领域的热点。
N2O5的合成方法主要有硝酸化学脱水法[1-2]、四氧化二氮臭氧氧化法[3-4]、FNO2-LiNO3[5]法和电解法(包括四氧化二氮电氧化法[6-7]和硝酸电解脱水法[8])。在这些方法中,N2O4电氧化法最具有工业化前景(电极反应如式(a)~(b)所示)。
阳极反应:N2O4+2HNO3→2N2O5+2H++2e- (a)
阴极反应:2HNO3+2H++2e-→N2O4+2H2O (b)
总反应:2HNO3→N2O5+H2O (c)
在N2O4电氧化合成N2O5过程中,工艺参数,如阳极液中N2O4初始浓度、电解液的循环速率、电解温度等对阳极反应有较大影响。然而,相关的研究报道却很少。本实验在恒电位条件下研究工艺参数对电解合成N2O5过程的影响规律。
2 实验部分 2.1 试剂与仪器98%浓硝酸(工业级, 山东化肥厂),N2O4(分析纯,天津赛美特特种气体有限公司),聚四氟乙烯隔膜(PTFE膜,孔径1.0 mm,厚度150 mm,北京塑料研究所)均为商购。以钛为基体的RuO2和IrO2二元金属氧化物涂层阳极(记为RuO2-IrO2/Ti)和IrO2单元金属氧化物涂层阴极(记为IrO2/Ti)采用热分解法制备,详细步骤参见文献[9]。
2.2 实验过程图 1是合成N2O5的电解装置示意图。电解槽为板框式,由不锈钢制成,内衬聚四氟乙烯,阳极室和阴极室容积均为20 mL。电解槽带冷却夹套,内通冷却乙醇以控制反应温度。实验采用10 V的直流电源,恒电压操作。首先向阴极储罐中加入浓HNO3,向阳极储罐加入N2O4浓度为25%~45%(w%,下同)的N2O4硝酸溶液。然后用聚四氟乙烯隔膜泵将阴、阳极储罐中的原料液送入阴、阳极室进行电解。电解后的阴、阳极液分别循环返回阴、阳极储罐。电解时间4 h,电解过程中每隔1 h取样,分析阴、阳极液的组成。
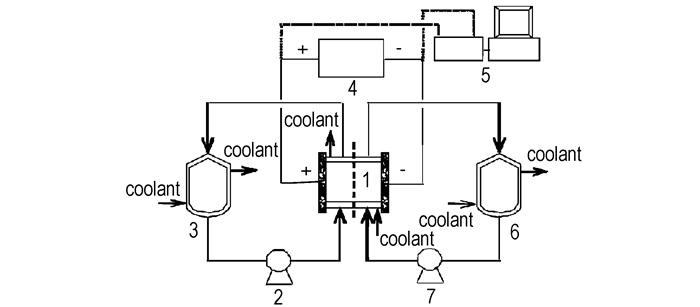
|
图 1 电解装置示意图 1—电解槽,2,7—泵,3,6—阳极液和阴极液储罐,4—直流电源,5—电化学工作站 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of experimental set-up 1—electrolyzer, 2, 7—pump, 3, 6—anolyte and catholyte reservoir, 4—DC power, 5—electrochemistry workstation |
采用氧化还原和总酸度两步滴定法测定阳极液和阴极液组成[9]。根据式(1)~(3)计算N2O5电流效率N、比能W和N2O5收率Y。
| $ N=\frac{{{m}_{{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\rm{/}{{M}_{{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}{Q/F}\times 100% $ | (1) |
| $ W=\frac{U\times I\times t}{{{m}_{{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}\times {{10}^{3}} $ | (2) |
| $ Y=\frac{{{m}_{{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}}}\rm{/}{{M}_{{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{5}}}}}}{2m_{{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}}^{0}\rm{/}{{M}_{{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}}}}\times 100% $ | (3) |
式(1)~(3)中,N为电流效率;W为比能,kW·h/kg N2O5;Y为N2O5收率;mN2O5为生成的N2O5量,g;m0N2O4为N2O4的加入量,g;Q为反应过程中通过的电量,C;F为法拉第常数,96485 C·mol-1;U为电解电压,V;I为电流,A;t为电解时间,h。
3 结果与讨论 3.1 阳极液中N2O4初始浓度的影响图 2为电流效率、比能和N2O5收率随阳极液中N2O4初始浓度的变化曲线。由图 2可见,电流效率随阳极液中N2O4初始浓度的升高而升高,当阳极液中N2O4初始浓度达到45%时,电流效率基本恒定,不再升高。比能的变化与电流效率的变化相反。N2O4初始浓度小于45%时,比能随阳极液中N2O4初始浓度下降,当N2O4浓度增加到45%以后,比能不再下降。在同样的温度条件下,N2O4的电导率远高于硝酸的电导率,增加阳极液中N2O4的浓度,可减小阳极液的电阻,使电流效率升高、比能下降。当N2O4浓度接近饱和时,阳极液电阻不再变化,电流效率和比能均趋于恒定。
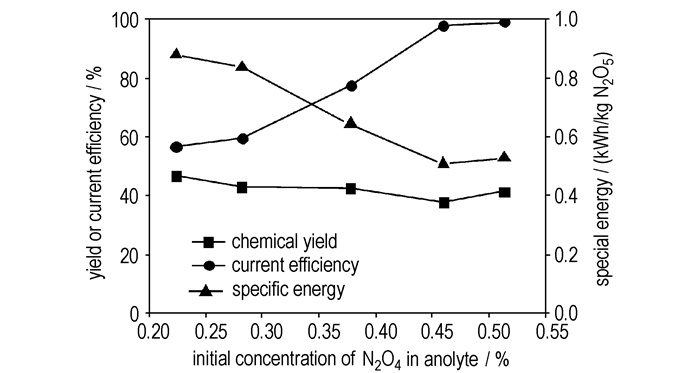
|
图 2 阳极液中N2O4初始浓度对电解合成N2O5过程的影响 (6 ℃,阳极液流量为20 mL·min-1) Fig.2 Influence of initial concentration of N2O4 in anolyte solution on the electrosynthesis of N2O5 (6 ℃, flow rate of anolyte is 20 mL·min-1) |
在本研究条件下,阳极液中N2O4的初始浓度对N2O5的收率无影响。
3.2 电解液流量的影响图 3为电流效率,比能和N2O5收率随电解液流量的变化曲线。由图 3可见,电解液循环流量提高,电流效率和N2O5收率明显提高、比能下降。表明,增大电解液循环流量,可以强化电氧化反应。陈志强[10]研究了反应(a)的机理后认为,在反应的前期,阳极反应(a)受动力学和传质共同控制,随着反应的进行,反应动力学逐渐成为控速步。因此,电解液循环流量对反应的强化作用主要体现在,较高的电解液流量可促进电解液的湍动、减少浓差极化。
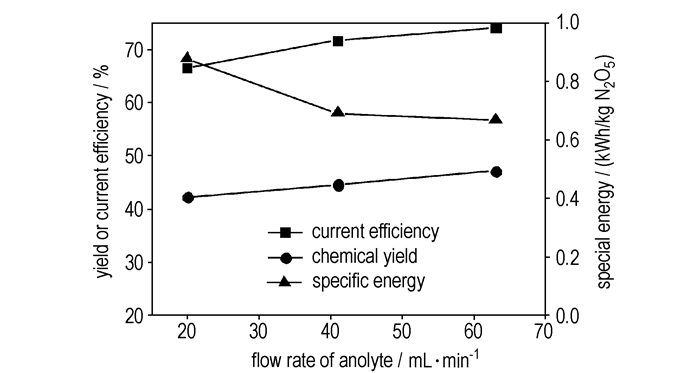
|
图 3 电解液流量对电解合成N2O5的影响 (6 ℃,N2O4初始浓度为28.2%) Fig.3 Influence of the flow rate of anolyte on the electrosynthesis of N2O5 (6 ℃, initial concentration of N2O4 in anolyte solution is 28.2%) |
如图 4所示,电解温度对电流效率,比能和N2O5收率的影响规律不同。电解温度升高,电流效率和N2O5收率均是先升高而后降低,在温度为6 ℃时达到最大值。比能随电解温度的变化趋势与此相反,是先降低而后升高,温度为6 ℃时最低。
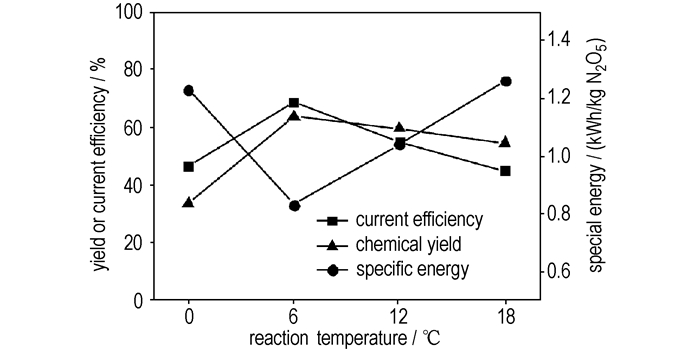
|
图 4 反应温度对电解合成N2O5的影响 (电解液流量为20 mL·min-1,N2O4初始浓度为28.2%) Fig.4 Influence of temperature on the electrosynthesis of N2O5 (flow rate of anolyte is 20 mL·min-1, initial concentration of N2O4 in anolyte solution is 28.2%) |
温度对电解过程的影响较为复杂。首先,温度影响N2O4电氧化反应速率。升高温度可加快反应速率,对电解合成N2O5有利。其次,温度影响理论分解电压。根据能斯特(Nernst)方程,升高温度可以提高电化学反应的理论分解电压。在相同的槽电压条件下,可以抑制析氧副反应,增加产物N2O5的收率。另外,温度影响电解液的电导率。升高温度,电解液的电导率增大,使溶液中的离子迁移速度加快,对电氧化反应有利。图 5为电解过程中在线监测得到的不同温度下的电流密度。可见,电流密度随温度升高而增大。而电流密度增加,有利于电氧化过程。
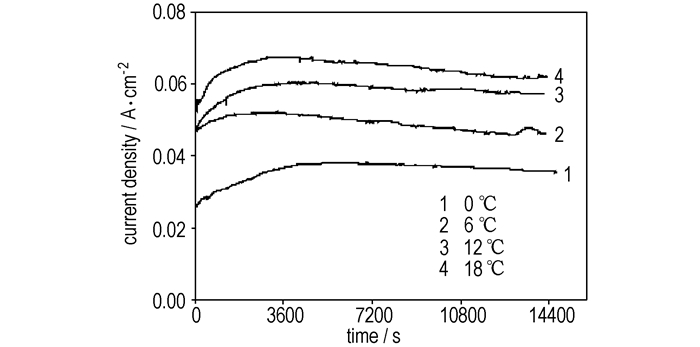
|
图 5 不同温度下电流密度随时间的变化曲线 (电解液流量为20 mL·min-1,N2O4初始浓度为28.2%) Fig.5 Current density-time curve for the electro-synthesis of N2O5 at different temperature (flow rate of anolyte is 20 mL·min-1, initial concentration of N2O4 in anolyte solution is 28.2%) |
最后,温度影响N2O5的分解速率。研究表明[11],N2O5的分解速率是温度的强函数,温度从15 ℃增加到20 ℃,N2O5在硝酸溶液中的分解速率增加近1倍。
综合温度对电氧化合成N2O5正、负两方面的影响,较适宜的温度为6 ℃。
4 结论以RuO2-IrO2/Ti为阳极,IrO2/Ti为阴极,多孔PTFE膜为隔膜,在恒电压条件下实验研究了阳极液中N2O4初始浓度、电解液流量和电解温度对合成N2O5过程的影响。阳极液中N2O4浓度和电解液循环流量增高,有利于提高电流效率、降低比能,但当阳极液中N2O4初始浓度达到45%、电解液循环流量超过41 mL·min-1后,电流效率和比能均趋于恒定。N2O5收率随电解液循环流量增加而增加,随阳极液中N2O4初始浓度的变化很小。适宜的阳极液N2O4初始浓度和电解液循环流量分别是45%和63 mL·min-1。电解温度主要影响电化学反应速率、电解液的电导率、理论电极电位和N2O5的分解速率,因而存在最佳的电解温度。在本研究范围内,该最佳温度为6 ℃。
| [1] |
吕春绪. N2O5绿色硝化及其新进展[J].
含能材料, 2010, 18(6): 611-617. Lü Chun-xu. Clean nitrating agent dinitrogen pentoxide and its application in nitration[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2010, 18(6): 611-617. |
| [2] |
苏敏, 王庆法, 张香文, 等. 新型绿色硝化剂N2O5的电化学合成研究进展[J].
含能材料, 2006, 14(1): 66-69. SU Min, WANG Qing-fa, ZHANG Xiang-wen, et al. Progress in electrochemical synthesis of a new green nitrating agent of dinitrogen pentoxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2006, 14(1): 66-69. |
| [3] |
Devendorf T E, Stacy J R. Pilot-plant-scale continuous manufacturing of solid dinitrogen pentoxide[C]//Albright L F, Carr R V C, Schmitt R J. ACS Symposius Series. Washington, DC: American Chemistry Society, 1996, 623: 68-77.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285701492_Pilot-Plant-Scale_Continuous_Manufacturing_of_Solid_Dinitrogen_Pentoxide |
| [4] |
Talawar M B, Sivabalan R, Polke B G, et al. Establishment of process technology for the manufacture of dinitrogen pentoxide and its utility for the synthesis of most powerful explosive of today-CL-20[J].
Journal of Hazardous Materials B, 2005, 124: 153-164. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.04.021 |
| [5] |
Fischer J W.
The Chemistry of Dinitrogen Pentoxide[M]. Nitro compound. USA: John Wiley & Sons, 1990: 267-365. |
| [6] |
Harrar J E, Pearson R K. Electrosynthesis of N2O5 by controlled-potential oxidation of N2O4 in anhydrous HNO3[J].
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1983, 130(1): 108-112. DOI:10.1149/1.2119632 |
| [7] |
Harrar J E, Quong R, Rigdon L P, et al. Scale-up studies of the electrosynthesis of dinitrogen pentoxide in nitric acid[J].
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(6): 2032-2044. DOI:10.1149/1.1837739 |
| [8] |
Peter C F. Electrochemical dehydration of nitric acid to dinitrogen pentoxide: UK, GB 2223031[P]. 1990-05-28.
|
| [9] |
Wang Qing-fa, Su Min, Zhang Xiang-wen, et al. Electrochemical synthesis of N2O5 by oxidation of N2O4 in nitric acid with PTFE membrane[J].
Electrochimica Acta, 2007(52): 3667-3672. |
| [10] |
陈志强. 电氧化合成五氧化二氮电极和隔膜的制备及性能研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2010.
CHEN Zhi-qiang. The preparation and peeformance of electrode and membrane for the electro-oxidation synthesis of N2O5[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2010. |
| [11] |
祝永刚. N2O4-N2O5-HNO3体系相平衡及N2O5分解动力学[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2009.
ZHU Yong-gang. Phase equilibria of N2O4-N2O5-HNO3 system and kinetics of N2O5 decomposition[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10056-2010092011.htm |
Dinitrogen pentoxide was prepared by the electro-oxidation of tetroxide dinitrogen in anhydrous nitric acid on the RuO2-IrO2/Ti anode.




