2. School of Chemical Engineering, Northwest University, Xi′an 710069, China
2. 西北大学化工学院,陕西 西安 710069
1, 1-Diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7) is a novel high-energy material with high thermal stability and low sensitivity to impact and friction. It has a density of 1.885 g·cm-3, a heat of formation of 133.7 kJ·mol-1, a same insensitivity to TATB (1, 3, 5-triamino-2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene) and a similar energy density with RDX (1, 3, 5-trinitroperhydro-1, 3, 5-triazine) and HMX (cyclotetramethylene tetranitramine)[1]. Since firstly synthesized in 1998[1], FOX-7 has received much attentions as the main component used in insensitive ammunitions and solid propellants. Many researches have been carried out on the synthesis, mechanism, molecule structure, thermal behavior, explosion performance and application of FOX-7[1-21]. FOX-7 is a representative "push-pull" nitro-enamine compound, which possesses a highly polarized carbon-carbon double bond with positive and negative charges stabilized by the amino group and nitro group respectively, and presents certain acidic properties[10, 22]. So, FOX-7 can react with strong alkalis to prepare some energetic salts, such as potassium salt, rubidium salt, cesium salt and guanidine salt[23-26]. Other salts and metal complexes of FOX-7 also can be synthesized through replacement reaction. Garg S[27-28] and He F[30] et al reported Ag(amine)(FOX-7) [amine: ammonia, methylamine and propylamine], Cu(amine)2(FOX-7)2 [amine: ammonia, methylamine, propylamine and dimethylamine, ethylenediamine and 1, 3-propane diamine] and other copper (nickel) bipyridyl (phenanthroline) FOX-7 complexes. In this paper, new zinc-FOX-7 complex was firstly synthsized, and its crystal structure and thermal behavior were studied by X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetry methods.
2 Experimental 2.1 Synthesis of the title complexK(FOX-7)·H2O (0.01 mol, 1.88 g) was put into excess 67% ethylenediamine (15 mL) to clear solution, and then Zn(NO3)2·6H2O (0.005 mol, 1.49 g) was added to it. After reaction at room temperature for 20 min, the resulting mixture was stored at room temperature for some time. Then many yellow crystals of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 were formed, which were filtered, washed with water and dried under vacuum. IR (KBr, ν/cm-1): 3414, 3332, 3294, 2943, 2883, 1641, 1493, 1354, 1247, 1132, 1012, 828, 750, 629, 504. Elemental anal: calcd.(%) for C10H30N14O8Zn: C 22.25, H 5.60, N 36.32; found: C 22.19, H 5.71, N 36.25.
2.2 Determination of the single crystal structureA light yellow crystal with dimensions of 0.35 mm×0.21 mm×0.19 mm was chosen for X-ray determination. The data were collected on a Bruker SMART APEX CCD X-ray diffractometer using graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation (λ=0.71073Å). The structure were solved by the direct methods (SHELXTL-97) and refined by the full-matrix-block least-squares method on F2 with anisotropic thermal parameters for all non-hydrogen atoms[31-32]. The hydrogen atoms were added according to the theoretical molecular models. Crystal data and refinement results are summarized in Table 1(CCDC No.: 946932.).
| Tab.1 Crystal data and structure refinement details for [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 |
The differential scanning calorimetry(DSC) was performed using a DSC 200F3 apparatus (NETZSCH, Germany) under a nitrogen atmosphere at a flow rate of 80 mL·min-1. The sample mass used in experiment was about 0.6 mg. The heating rates were 5.0, 7.5, 10.0, 12.5, 15 ℃·min-1, respectively, and temperature range was from room temperature to 450 ℃.
The thermogravimetry was performed using a SDT-Q600 apparatus (TA, USA) under nitrogen at a flow rate of 100.0 mL·min-1. The sample mass was 0.76 mg and heating rate was 10.0 ℃·min-1. Temperature range was from room temperature to 450 ℃.
The impact sensitivity was determined based on GB/T21567-2008 by using a ZBL-B impact sensitivity instrument (Nachen Co., China). The mass of drop wight is 2.0 kg. The sample mass for each test is 30 mg.
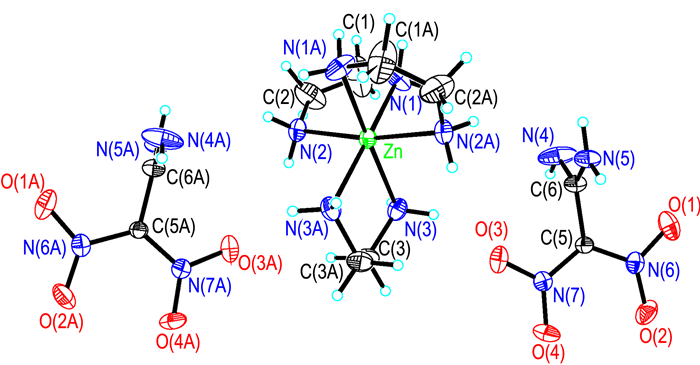
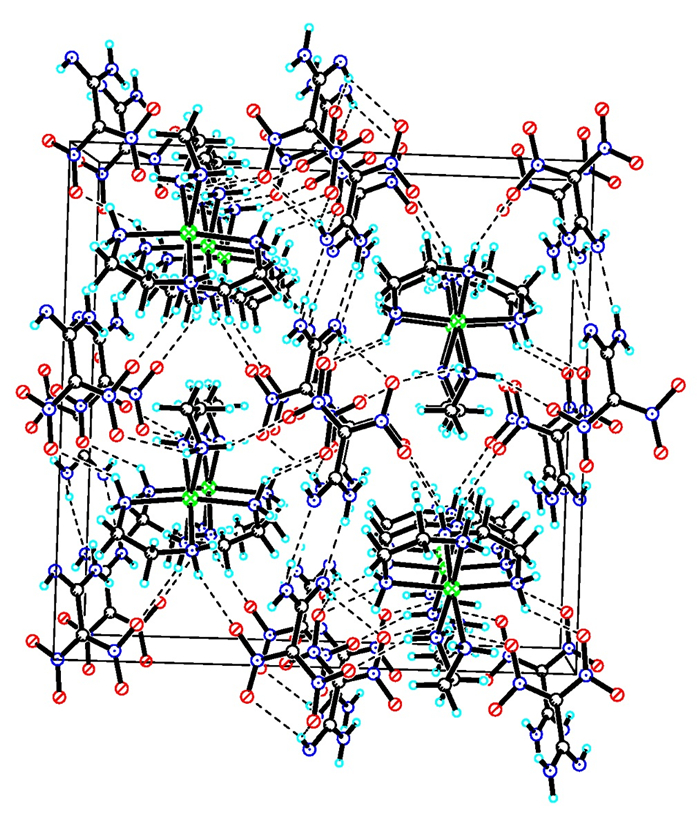
3 Results and discussion 3.1 Crystal structureCrystal structure and crystal packing of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 are illustrated in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. Selected bond lengths and bond angles of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 are summarized in Table 2.
|
Fig.1 Crystal structure of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 with 30% probability level |
|
Fig.2 Packing of molecular [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 in crystal lattice |
| Tab.2 Selected bond lengths (nm) and bond angles (°) |
[Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with space group C2/c containing four molecules per unit cell. As shown in Fig. 1, [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 is formed of one [Zn(en)]32+ ion and two FOX-7- anions. The whole complex exhibits a centrosymmetric structure around Zn2+ ion (symmetry transformation: -x, y, -z+1/2). Central Zn2+ ion is coordinated by six N atoms from three ethylenediamine molecules, and two FOX-7- anions symmetrically distribute in both sides of [Zn(en)]32+ ion and have no coordination with central Zn2+ ion. Six N atoms around central Zn2+ ion form a distorted octahedral structure. At first, we predict the complex should be Zn(en)(FOX-7)2 including one ethylenediamine molecule or Zn(en)2(FOX-7)2 including two ethylenediamine molecules, and two FOX-7- anion should be involved in coordination, but the result is unexpected. It is different from that of analogous Zn(NH3)2(FOX-7)2, which is a four-coordination structure, two FOX-7- anions all have coordination with central Zn2+ ion[33]. According to the structure of analogous Cu(en)2(FOX-7)2(H2O)2[28], the coordination structure of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 is reasonable. In addition, there are six kinds of N—H…O hydrogen-bond interactions and one kind of N—H…N hydrogen-bond interaction in [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2. It is the coordination interactions, electrostatic attractions and hydrogen-bond interactions that form the order crystal packing of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 (Fig. 2).
To [Zn(en)3]2+, three ethylenediamine molecules exhibit different configurations because of different positions and hydrogen-bond interactions, supporting by the bond lengths [Zn(1)—N(1)(0.2228 nm), Zn(1)—N(2) (0.2177 nm) and Zn(1)—N(3) (0.2201 nm)] and bond angles [N(2)—Zn(1)—N(2)A (170.49°), N(2)—Zn(1)—N(3) (91.89°) N(2)A—Zn(1)—N(3) (95.36°), N(3)—Zn(1)—N(3)A (80.51°), N(2)—Zn(1)—N(1)A (94.25°), N(3)—Zn(1)—N(1)A (172.44°), N(2)—Zn(1)—N(1) (79.03°), N(3)—Zn(1)—N(1)(94.51°), N(1)A—Zn(1)—N(1)(90.99°)]. The self-symmetry ethylenediamine molecule presents greater distortion than other two symmetric ethylenediamine molecules, according to the bond lengths of C(1)—C(2)(0.1361 nm) and C(3)—C(3)A(0.1509 nm), bond angles of N(2)—Zn(1)—N(1)(79.03°) and N(3)—Zn(1)—N(3)A (80.51°), and torsion angles of N(3)—C(3)—C(3)A—N(3)A (-57.8°) and N(2)—C(2)—C(1)—N(1)(14.1°).
The space configuration of FOX-7- anion changes from one plane to two approximate orthogonal planes (no-hydrogen atoms)[2], according to the torsion angles of N(4)—C(6)—C(5)—N(7) (-96.0°), N(5)—C(6)—C(5)—N(7) (84.9°), N(4)—C(6)—C(5)—N(6) (-87.3°) and N(5)—C(6)—C(5)—N(6) (-91.9°), and the intersection of the two approximate orthogonal planes is C(5)—C(6) bond, which can also be found in other salts of FOX-7[23-24]. The bond lengths and bond angles change greatly from molecular state to ionic state. The oretical C(5)—C(6) double bond (0.1498 nm) in FOX-7- anion is much closer to C—C single bond (0.153 nm) than that in FOX-7 molecule. Equilong C(6)—N(4) and C(6)—N(5) bonds present big deviation (0.1299 and 0.1333 nm). C(6)—N(4) in FOX-7- anion is a typical C—N double bond. FOX-7 has changed into its one tautomer format.
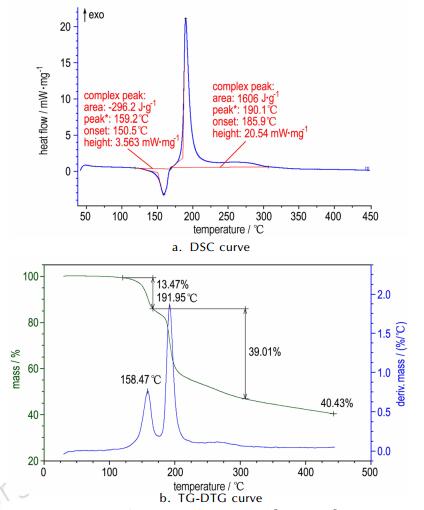
3.2 Thermal behaviorTypical DSC and TG-DTG curves in Fig. 3 indicate that the thermal decomposition behavior of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 can be divided into two obvious stages. The first stage is an endothermic melting-decomposition process, which occurs at 120~165 ℃ with a mass loss of about 13.5%, which is consistent with the theoretical value (11.2%) of losing one ethylenediamine molecule. The extrapolated onset temperature, peak temperature and decomposition enthalpy of the process are 150.5, 159.2 ℃ and 296.2 J·g-1 at a heating rate of 10.0 ℃·min-1, respectively. The second stage is an intense exothermic decomposition process with a mass loss of about 32.1% at 165~310 ℃, and the extrapolated onset temperature, peak temperature and decomposition enthalpy of the process are185.9 ℃, 190.1 ℃ and -1606 J·g-1 at a heating rate of 10.0 ℃·min-1, respectively. The final residue at 450 ℃ is about 40.4%, which should contain ZnO(15.2%) and some organic matters. The thermal behavior of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 is much different from that of Zn(NH3)2(FOX-7)2, which exhibits two continuous exothermic decomposition processes without melting process, and the extrapolated onset temperature and peak temperature of the first decomposition are 198.1 ℃ and 204.4 ℃, respectively, at a heating rate of 10.0 ℃ ·min-1[33]. It shows the thermal stability of Zn(NH3)2(FOX-7)2 is better than that of [Zn(en)2](FOX-7)2.
|
Fig.3 DSC (a) and TG/DTG (b) curves of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 at a heating rate of 10.0 ℃ ·min-1 |
A multiple heating method was employed to obtain the kinetic parameters (apparent activation energy (E) and pre-exponential constant (A)) of the exothermic decomposition (Table 3). The calculated results in table 3 indicate that the apparent activation energy obtained by Kissinger method(Ek) is consistent with that by Ozawa method(Eo)[34-35]. The linear correlation coefficients (rk and ro) are all close to 1. Moreover, the apparent activation energy of the exothermic decomposition process is low, indicating that [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 is easy to exothermically decompose at temperature above 165 ℃.
| Tab.3 Te, Tp and kinetic parameters of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 at various heating rates |
The self-accelerating decomposition temperature (TSADT) and critical temperature of thermal explosion (Tb) are two important parameters for energetic materials, which are required to ensure safe storage and process operations and then to evaluate the thermal stability. TSADT and Tb can be obtained by Eq.(1) and Eq.(2)[36-37], respectively.
| $ {T_{\rm SADT}} = {T_{{\rm{e}}0}} = {T_{{\rm{e}}i}} - n{\beta _i} - m\beta ^2_i\;\;\;\;i = 1 - 5 $ | (1) |
| $ {T_{\rm{b}}} = {\rm{ }}\frac{{{E_{\rm{O}}} - {\rm{ }}\sqrt {E^2_{\rm{O}} - 4{E_{\rm{O}}}R{T_{{\rm{e}}0}}} }}{{2R}} $ | (2) |
where R is the gas constant; Te0 is the value of Te corresponding to β→0; n and m are coefficients.
TSADT and Tb for [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 are 167.1 ℃ and 168.8 ℃, respectively, which are much lower than those of Zn(NH3)2(FOX-7)2 (183.2 ℃ and 195.8 ℃)[33].
3.4 SensitivityThe experimental results indicate that the characteristic drop-height of impact sensitivity(H50) of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 is 105 cm (about 20.6 J), which is much lower than that of Zn(NH3)2(FOX-7)2 (9 J) and RDX(7.4 J)[33, 38].
4 Conclusions(1) [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 was first synthesized and structurally determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The crystal of [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 is the monoclinic crystal system with space group C2/c. Central Zn2+ ion is coordinated by six N atoms from three ethylenediamine molecules to form a distorted octahedral structure, and while FOX-7- anion has no coordination with central Zn2+ ion.
(2) The thermal decomposition of [[Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 exhibits two processes. The apparent activation energy and pre-exponential constant of the exothermic decomposition process are 137.7 kJ·mol-1, and 1013.65 s-1, respectively. [Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 is easy to exothermically decompose at temperature above 165 ℃, and relatively less sensitive.
| [1] |
Latypov N V, Bergman J, Langlet A, et al. Synthesis and reaction of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene[J]. Tetrahedron, 1998, 54: 11525-11536. DOI:10.1016/S0040-4020(98)00673-5 |
| [2] |
Bemm U, Östmark H. 1, 1-Diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene: a novel energetic material with infinite layers in two dimensions[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section C, 1998, 54: 1997-1999. |
| [3] |
Gindulyt A, Massa L, Huang L, et al. Proposed mechanism of 1, 1-diamino-dinitroethylene decomposition: A density functional theory study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 1999, 103(50): 11045-11051. DOI:10.1021/jp991794a |
| [4] |
JI Guang-fu, XIAO Hei-ming, DONG Hai-shan, et al. The theoretical study on structure and property of diaminodinitroethylene[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2001, 59(1): 39-47. |
| [5] |
Bellamy A J, Goede P, Sandberg C, et al. Substitution reactions of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene(FOX-7)[C]//33th Int Annu Conf ICT, 2002.
|
| [6] |
Sorescu D C, Boatz J A, Thompson D L. First-principles calculations of the adsorption of nitromethane and 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene(FOX-7) molecules on the Al(111) surface[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2003, 107: 8953-8964. DOI:10.1021/jp030258m |
| [7] |
CAI Hua-qiang, SHU Yuan-jie, YU Wei-fei, et al. Study on synthesis of FOX-7 and its reaction mechanism[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2004, 62(3): 295-301. |
| [8] |
Cai H Q, Shu Y J, Huang H, et al. Study on reactions of 2-(dinitromethylene)-4, 5-imidazolidinedione[J]. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2004, 69: 4369-4374. DOI:10.1021/jo030395f |
| [9] |
Sorescu D C, Boatz J A, Thompson D L. First-principles calculations of the adsorption of nitromethane and 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene (FOX-7) molecules on the r-Al2O3(0001) surface[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109: 1451-1463. DOI:10.1021/jp046193k |
| [10] |
Herve G, Guy J, Latypov N. The reactivity of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethene (FOX-7)[J]. Tetrahedron, 2005, 61: 6743-6748. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2005.05.010 |
| [11] |
Trzciński W A, Cudzilo S, Chylek Z, et al. Detonation properties of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethene (DADNE)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 157: 605-612. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.026 |
| [12] |
Anniyappan M, Talawar M B, Gore G M, et al. Synthesis, characterization and thermolysis of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene(FOX-7) and its salts[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 137: 812-819. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.03.034 |
| [13] |
Gao H X, Zhao F Q, Hu R Z, et al. Thermochemical properties, thermal behavior and decomposition mechanism of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2dinitroethylene (DADE)[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2006, 24: 177-181. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1614-7065 |
| [14] |
Zerilli F J, Kuklja M M. First principles calculation of the mechanical compression of two organic molecular crystals[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2006, 110: 5173-5179. DOI:10.1021/jp0605754 |
| [15] |
Zerilli F J, Kuklja M M. Ab initio equation of state of an organic molecular crystal: 1, 1-Diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2007, 111(9): 1721-1725. DOI:10.1021/jp067709y |
| [16] |
Sizova E V, Sizov V V, Tselinskii I V. 1, 1, 2, 2-Tetraaminoethane derivatives:Ⅲ.condensation of 2-(Dinitromethylene) imidazolidine-4, 5-diol with nitrogen-containing nucleophiles[J]. Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2007, 43(8): 1232-1237. DOI:10.1134/S107042800708026X |
| [17] |
Fan X Z, Li J Z, Liu Z R. Thermal behavior of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2007, 111: 13291-13295. DOI:10.1021/jp075889l |
| [18] |
Zhao J J, Liu H. High-pressure behavior of crystalline FOX-7 by density functional theory calculations[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2008, 42: 698-703. DOI:10.1016/j.commatsci.2007.10.008 |
| [19] |
Buszewski B, Michel M, Cudzilo S, et al. High performance liquid chromatography of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethene and some intermediate products of its synthesis[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 164: 1051-1058. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.018 |
| [20] |
Xing X L, Xue L, Zhao F Q, et al. Thermochemical properties of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene(FOX-7) in dimethyl sulfoxide(DMSO)[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2009, 491: 35-38. DOI:10.1016/j.tca.2009.02.019 |
| [21] |
Ahn J H, Kim J K, Kim H S, et al. Solubility of 1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethylene in N, N-dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, and N-nethyl-2-pyrrolidone[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering Data, 2009, 54: 3259-3260. DOI:10.1021/je900235s |
| [22] |
Rajappa S. Nitroenamines preparation, structure and synthetic potential[J]. Tetrahedron, 1981, 37: 1453-1480. DOI:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)92085-X |
| [23] |
Xu K Z, Chang C R, Song J R, et al. Preparation, crystal structure and theoretical calculation of G(FOX-7)[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 2008, 26: 495-499. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1614-7065 |
| [24] |
XU Kang-zhen, ZUO Xian-gang, SONG Ji-rong, et al. The synthesis, molecular structure and thermal behavior of K(FOX-7)·H2O[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(4): 638-643. |
| [25] |
Luo J A, Xu K Z, Wang M, et al. Syntheses and thermal behaviors of Rb(FOX-7)·H2O and Cs(FOX-7)·H2O[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemistry Society, 2010, 31(10): 2867-2872. DOI:10.5012/bkcs.2010.31.10.2867 |
| [26] |
Xu K Z, Song J R, Zhao F Q, et al. Thermal behavior, specific heat capacity and adiabatic time-to-explosion of G(FOX-7)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 158: 333-339. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.077 |
| [27] |
Garg S, Gao H X, Joo Y H, et al. Taming of the silver FOX[J]. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2010, 132: 8888-8890. DOI:10.1021/ja103935q |
| [28] |
Garg S, Gao H X, Parrish D A, et al. FOX-7 (1, 1-diamino-2, 2-dinitroethene): trapped by copper and amines[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2011, 50: 390-395. DOI:10.1021/ic102136r |
| [29] |
Vo T T, Parrish D A, Shreeve J M. 1, 1-Diamino-2, 2-dintroethene (FOX-7) in copper and nickel diamine complexes and copper FOX-7[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2012, 51: 1963-1968. DOI:10.1021/ic202288t |
| [30] |
He F, Xu K. Z, Zhang H, et al. Two new copper-FOX-7 complexes: synthesis, crystal structure, and thermal behavior[J]. Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 2013, 66(5): 845-855. DOI:10.1080/00958972.2013.771182 |
| [31] |
Sheldrick G M. SHELXS[CP], University of Göttingen, Germany, 1997.
|
| [32] |
Sheldrick G M. SHELXL, Program for X-ray Crystal Structure Refinement[CP], University of Göttingen, Germany, 1997.
|
| [33] |
Gao Z, Huang J, Xu K Z. et al, Synthesis, structural characterization and thermal properties of a new energetic zinc-FOX-7 complex[J]. Journal of Coordintion Chemistry, 2013, 66(20): 3572-3580. DOI:10.1080/00958972.2013.848276 |
| [34] |
Kissinger H E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1957, 29: 1702-1706. DOI:10.1021/ac60131a045 |
| [35] |
Ozawa T. A method of analying thermogravimetric data[J]. Bulletin of Chemical Society Jpn, 1965, 38: 1881-1886. DOI:10.1246/bcsj.38.1881 |
| [36] |
Hu R Z, Gao S L, Zhao F Q, et al. Thermal Analysis Kinetics[M]. 2th, Beijing: Science Press, 2008.
|
| [37] |
Zhang T. L, Hu R. Z, Xie Y, et al. The estimation of critical temperatures of thermal explosion for energetic materials using non-isothermal DSC[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 1994, 244: 171-176. DOI:10.1016/0040-6031(94)80216-5 |
| [38] |
Tian Y D, Zhao F Q, Liu J H. Handbook of Energetic Materials and the Related Compounds[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2011.
|
[Zn(en)3](FOX-7)2 was firstly synthesized and characterized. Its thermal decomposition behavior was studied by TG-DTG and DSC methods.




