2. 北京动力机械研究所, 北京 100074
2. Beijing Power Machinery Research Institute, Beijing 100074, China
设计合成新型高能量、高安全性的环境友好型含能化合物一直是含能材料工作者的研究重点[1-3]。高氮四唑类化合物由于结构中含有大量的N—N和C—N键, 具有较高的生成焓, 且其独特的芳香结构五元杂环中C、N原子均采用sp2杂化, 形成离域大π键, 使之形成共轭体系, 提高了化合物的热稳定性, 降低了其机械感度[4-6]。同时四唑类化合物普遍N含量较高, C、H含量较低, 改善了氧平衡, 使其具有较大的产气量, 且其分解产物主要为N2, 对环境无污染, 在构筑新型高能量密度化合物方面具有广阔前景[7-9]。Klapötke等在2012年基于Tselinskii等[10]的合成方法制备了1, 1′-二羟基-5, 5′-联四唑 (BTO), 并制备出了高能钝感的5, 5′-联四唑-1, 1′-二氧二羟铵盐 (TKX-50), 有望作为RDX的取代物应用在军事领域[11]。2013年Klapötke等[12]又报道了BTO部分碱金属盐与碱土金属盐的合成、晶体结构及在烟火药领域的应用等研究。毕福强[13]也于2015年对部分碱金属盐溶解度等相关性能进行报道, 其中钾盐可以作为潜在的消焰剂应用, 同时钾盐可以作为新型火工药剂应用在起爆药领域。此外, 作为碱金属元素, 铷的化学活泼性高于钾, 1, 1′-二羟基-5, 5′-联四唑铷盐 (BTORb) 在起爆药和烟火药等含能材料领域也有应用前景, 而其合成、晶体结构及性能则未见报道, 同时对其在应用方面的探索也相应缺乏。
基于此, 本研究以1, 1′-二羟基-5, 5′-联四唑 (BTO) 为起始物质, 合成未见报道的新型含能材料——1, 1′-二羟基-5, 5′-联四唑铷 (BTORb) 并表征, 首次培养获得BTORb的单晶, 并利用X-射线单晶衍射仪对其晶体结构进行测定。采用差示扫描量热分析技术 (DSC) 和热重分析技术 (TG-DTG) 研究其热分解性能, 计算得到其非等温动力学参数和热爆炸临界温度等热力学参数。利用氧弹量热技术测定其燃烧热, 并计算其标准生成焓。测试了其撞击、摩擦及静电感度。
2 实验部分 2.1 试剂和仪器试剂:碳酸铷、乙二醛、盐酸羟胺、叠氮化钠、无水乙醚、无水甲醇, 国药集团化学试剂有限公司, 分析纯; BTO为实验室根据文献方法[11]自制, 实验用水为去离子水。
仪器及测试条件: Bruker SMART APEX CCD单晶衍射仪:石墨单色器单色化的Mo Kα射线 (λ=0.071073 nm) 光源, 测试温度298(2) K, 晶体结构通过直接法由SHELXS-97解析得到[14], 并由全矩阵最小二乘法精修由SHELXL-97程序完成[15]; Bruker D8Advance粉末衍射仪:石墨单色器单色化的Cu Kα射线 (λ=0.154439 nm) 光源, 所用电压40 kV, 电流40 mA, 收集范围5~50°, 步长0.03°; Perkin-Elmer公司Pyris-1型DSC分析仪和TG-DTG热重分析仪:流动N2气氛, 流速20 mL·min-1, 升温速率5 ℃·min-1, 测试范围0~500 ℃; Parr 6200全自动氧弹量热仪:选用1104型氧弹, 充氧1 min, 测试温度25 ℃, 相对湿度30%, 药量500 mg, 平行测试6次。
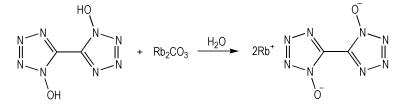
2.2 合成过程称取BTO 0.206 g (1 mmol) 溶解于10 mL去离子水中作为底液, 在75 ℃下加热搅拌, 称取碳酸铷0.229 g (1 mmol) 溶于5 mL去离子水中并缓慢滴加入底液, 反应60 min后冷却至室温, 过滤, 取少量母液培养晶体, 其余减压旋干, 得到白色固体用无水甲醇洗涤并旋干, 得到白色粉末产物0.277g, 产率82%。母液在室温下缓慢蒸发, 7天后得到可用于结构测定的透明块状晶体。合成路线见Scheme 1。13C NMR (d6-DMSO, 100 MHz): 161.28。MS (ESI-): 168.70 (C2N8O22-); MS (ESI+): 84.05 (Rb+)。IR (KBr, ν/cm-1): 3434.70, 2923.42, 2262.43, 2151.41, 2004.36, 1634.69, 1507.52, 1408.11, 1345.02, 1229.51, 1161.87, 1052.39, 994.38, 867.56, 797.13, 770.02, 731.68, 575.01, 497.85。Anal. calcd for C2Rb2N8O2(%)(337.84): C 7.09, N 33.05; C 7.04, N 33.11。
|
Scheme1 Synthesisrouteofdirubidium 5 , 5′-bis(tetrazole-1- oxide)(BTORb) |
选取尺寸为0.42 mm×0.35 mm×0.32 mm的晶体进行单晶衍射分析, 其晶体结构详细参数见表 1。该晶体参数被剑桥晶体结构数据中心保存 (CCDC, No.1405692)。结果表明其属于单斜晶系, 空间群P2(1)/n, 密度2.886 g·cm-3, 每个晶胞中含有4个分子。同时对其粉末样品进行X-射线粉末衍射 (P-XRD) 分析, 并与理论粉末衍射值进行对比。其晶体结构及粉末衍射图见图 1和图 2, 堆积图见图 3。表 2及表 3分别列出晶体结构的主要键长和键角。

|
图 1 BTORb的分子结构 Fig.1 Molecular structure of BTORb |

|
图 2 BTORb的粉末衍射图 Fig.2 The P-XRD patterns of BTORb |

|
图 3 BTORb沿b轴方向的晶胞堆积图 Fig.3 Packing diagram of BTORb atb-axis |
| 表 1 BTORb的晶体结构数据和结构精修参数 Tab.1 Crystal data and structure refinement details for BTORb |
| 表 2 BTORb的部分键长 Tab.2 Selected bond lengths for BTORb |
| 表 3 BTORb的部分键角 Tab.3 Selected bond angles for BTORb |
由图 1可知, BTO与Rb2CO3发生复分解反应, 失去两个羟基H, 成盐可表示为 (Rb+)2(BTO)2-。BTO2-同时起螯合配体与桥联配体的作用, 四唑环中N (8)、O (1) 与Rb (1), N (4)、O (2) 与Rb (2) 分别构成螯合配位结构, 同时四唑环两侧N、O原子分别与不同的Rb+配位, 形成桥联结构。Rb (1) 与来自4个BTO配体上的N原子和O原子发生配位, 形成8配位结构。由粉末衍射图可知, 通过粉末样品得到的衍射曲线与通过晶体结构得到的理论衍射曲线彼此接近, 峰位置一致, 峰强度相近, 说明制备得到的BTORb粉末样品与培养得到的BTORb晶体样品一致。由图 3可知BTORb为网状堆积结构, 不同片层的BTO2-与Rb+片层交替排列, 构成三维网状结构。由于BTORb晶体中不含水, 其结构中原子之间排列致密, 使其晶体密度较高, 高于锂盐 (1.765 g·cm-3) 和钠盐 (1.767 g·cm-3), 仅次于铯盐 (3.285 g·cm-3)。其结构相对于锂盐和钠盐更稳定。
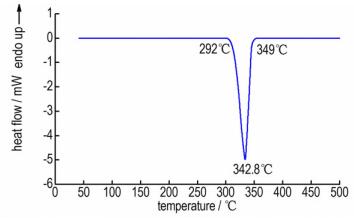
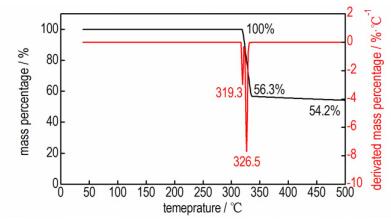
3.2 热行为及标准生成焓5 ℃·min-1下BTORb的热分解DSC及TG-DTG曲线如图 4、图 5所示, 由图 4、图 5可知BTORb主要存在一个明显的放热分解过程, 放热阶段出现在292~349 ℃, 峰温为342.8 ℃。由TG-DTG曲线可知, BTORb盐在较小温度范围内存在一个较剧烈的分解失重过程:升温至302 ℃时BTORb开始失重, 至346 ℃时剩余质量为56.3%, 质量损失为43.7%, 分别在319.3和326.5 ℃时达到最大失重率, 推测为BTO有机环的分解破坏。随温度升高, BTORb存在一个缓慢的热失重过程, 500 ℃时残留质量为54.2%。BTORb的固相分解过程起始温度高于250 ℃, 表明其热稳定性较好。由于BTORb结构中不含水, 其热稳定性优于锂盐和钠盐, 与钾盐热分解温度接近。
|
图 4 BTORb的DSC曲线 (5 ℃·min-1) Fig.4 DSC curve of BTORb at the heating rate of 5 ℃·min-1 |
|
图 5 BTORb的TG-DTG曲线 (5 ℃·min-1) Fig.5 TG-DTG curve of BTORb at the heating rate of 5 ℃·min |
燃烧热和生成焓是评价新型含能材料能量特性的重要参数。选择Parr公司1104型氧弹, 测定BTORb的定容燃烧热 (Qv) 为-4.165 MJ·kg-1。通过燃烧反应方程式 (1) 和计算式 (2) 得到其定压燃烧热 (ΔH) 为-1400.82 kJ·mol-1。
| $ \begin{array}{l} {{\rm{C}}_2}{\rm{R}}{{\rm{b}}_2}{{\rm{N}}_8}{{\rm{O}}_2}\left( {\rm{s}} \right) + 3/2{{\rm{O}}_2}\left( {\rm{g}} \right) \to {\rm{R}}{{\rm{b}}_2}{\rm{O}}\left( {\rm{s}} \right) + 2{\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_2}\left( {\rm{g}} \right)\\ + 4{{\rm{N}}_2}\left( {\rm{g}} \right) \end{array} $ | (1) |
| $ \Delta H = {Q_p} = {Q_v} + \Delta nRT $ | (2) |
通过已知的标准生成焓ΔfH298θ[Rb2O (s)]=-338.9 kJ·mol-1, ΔfH298θ[CO2(g)]=-393.5 kJ·mol-1[16], 通过 (3) 式计算BTORb的标准生成焓为ΔfH298θ=274.91 kJ·mol-1。
| $ \begin{array}{l} {\Delta _{\rm{f}}}H_{298}^{\rm{\theta }}\left( {{\rm{BTORb}}} \right) = {\Delta _{\rm{f}}}{H^{\rm{\theta }}}\left( {{\rm{R}}{{\rm{b}}_2}{\rm{O,s}}} \right) + \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;2{\Delta _{\rm{f}}}{H^{\rm{\theta }}}\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_2},{\rm{g}}} \right) - {\Delta _{\rm{c}}}{H^{\rm{\theta }}}\left( {\rm{s}} \right) \end{array} $ | (3) |
根据Kissinger法 (式 (4))[17]和Ozawa-Doyle法 (式 (5))[18]计算BTORb放热分解反应的表观活化能Ea和指前因子A, 测定其在不同线性升温速率 (5,10,15,20 ℃·min-1) 下的DSC曲线, 得到放热峰的峰温数据:
| $ \ln \left( {\frac{\beta }{{T_{\rm{p}}^2}}} \right) = \ln \left( {\frac{{{A_{\rm{K}}}R}}{{{E_{\rm{K}}}}}} \right) - \frac{{{E_{\rm{K}}}1}}{{R{T_{\rm{p}}}}} $ | (4) |
| $ \log \beta + \frac{{0.4567{E_{\rm{O}}}}}{{R{T_{\rm{p}}}}} = C $ | (5) |
式中,Tp为放热分解峰温, ℃, 由DSC曲线得到; R为气体常数, 8.314 J·mol-1·℃-1; β为线性升温速率, ℃·min-1; C为常数, 计算得到的非等温动力学参数列于表 4。
| 表 4 BTORb的放热分解峰温度及非等温动力学参数 Tab.4 Peak temperatures and non-isothermal kinetic parameters for the exothermic decomposition of BTORb |
由表 4可以看出, 通过两种方法计算得到的BTORb表观活化能结果相近, 分别为185.9 kJ·mol-1和186.7 kJ·mol-1, 且可以得到其热分解的Arrhenius方程为: lnk=13.51-186.3×103/RT, 其中k为非等温动力学反应速率常数。
含能材料的热安全性可通过热爆炸临界温度 (Tbp) 来评估。根据热爆炸临界温度估算式[19]:
| $ {T_{{\rm{pi}}}} = {T_{{\rm{p0}}}} + a\beta + b{\beta ^2} + c{\beta ^3} $ | (6) |
| $ {T_{{\rm{bp}}}} = \frac{{E - \sqrt {{E^2} - 4ER{T_{{\rm{p}}0}}} }}{{2R}} $ | (7) |
式中, Tpi为升温速率βi时的峰温; a、b、c为常数。计算得到BTORb的热爆炸临界温度Tbp为356.7 ℃, 表明其热安定性较好。
3.4 感度测试按照GJB5891.22-2006、GJB5891.24-2006以及GJB5891.27-2006, 对BTORb的撞击、摩擦以及静电感度进行测试。撞击感度测试条件为: 20 mg药量, 800 g落锤, 试验36发; 摩擦感度测试条件为70°摆角, 1.23 MPa, 20 mg药量, 两组平行试验; 静电感度测试条件为电容500 pF, 电极间隙0.12 mm, 串联电阻100 kΩ, 电压正负50 kV内联系可调, 试验用量22 mg, 松装, 测试25发, 两组平行试验。测试结果表明BTORb撞击感度H50为34.8 cm, 其摩擦感度发火百分数为36%, 静电火花感度50%发火能量为0.34 J。
4 结论(1) 以1, 1′-二羟基-5, 5′-联四唑为起始原料合成新型含能材料1, 1′-二羟基-5, 5′-联四唑铷 (BTORb), 收率82%, 并通过元素分析、红外光谱、核磁共振光谱和质谱对其进行表征。
(2) 首次培养得到并测定BTORb的单晶结构, 分析结果表明, 其属于单斜晶系, 空间群P2(1)/n, 密度2.886 g·cm-3, 中心Rb+与来自不同BTO配体的N、O原子形成8配位结构。不同片层的BTO配体与Rb+交替排列相互连接, 构成三维网状结构。
(3) 对BTORb的热分解过程进行分析, 结果表明其存在一个明显放热分解过程, 起始温度为292 ℃, 证明其热稳定性良好。计算得到其标准生成焓为274.91 kJ·mol-1。运用Kissinger法和Ozawa-Doyle法计算得其热分解Arrhenius方程为: lnk=13.51-186.3×103/RT。其热爆炸临界温度Tbp为356.7 ℃, 表明其热安定性较好。
(4) 对BTORb进行感度测试, 其撞击感度H50为34.8 cm, 摩擦感度发火百分数为36%, 静电火花感度50%发火能量为0.34 J。其感度性能适中, 有望作为新型钝感火工药剂应用于含能材料领域。
| [1] | YIN Ping, ZHANG Qing-hua, Shreeve J M. Dancing with energetic nitrogen atoms: versatile N-functionalization strategies for N-heterocyclic frameworks in high energy density materials[J]. Acc Chem Res, 2016, 49: 4-16. DOI:10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00477 |
| [2] | TANG Yong-xin, HE Chun-lin, Shreeve J M, et al. C—N bonded energetic bi-heterocyclic compounds with good detonation performance and high thermal stability[J]. J Mater Chem A, 2016, 4: 3879-3885. DOI:10.1039/C5TA09803C |
| [3] | ZHANG Jin, Shreeve J M. 3, 3'-Dinitroamino-4, 4'-azoxyfurazan and its derivatives: an assembly of diverse N—O building blocks for high performance energetic materials[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136: 4437-4445. DOI:10.1021/ja501176q |
| [4] |
张光全. 绿色四唑类起爆药研究的最新进展[J].
含能材料, 2011, 19(4): 473-478. ZHANG Guang-quan. Recent progress in green primary explosives[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials (Hanneng Cailiao), 2011, 19(4): 473-478. |
| [5] |
盛涤伦, 朱雅红, 蒲彦利. 新一代起爆药设计与合成研究进展[J].
含能材料, 2012, 20(3): 263-272. SHENG Di-lun, ZHU Ya-hong, PU Yan-li. Develpement of a new-generation primary explosive designing and synthesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials (Hanneng Cailiao), 2012, 20(3): 263-272. |
| [6] | Fischer D, Klapötke T M, Stierstorfer J. Potassium 1, 1'-dinitramino-5, 5'-bistetrazolate: a primary explosive with fase detonation and high initiation poewe[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2014, 53: 8172-8175. DOI:10.1002/anie.201404790 |
| [7] | Fischer D, Klapötke T M, Stierstorfer J. 1, 5-Di (nitramino) tetrazole: high sensitivity and superior explosive performance[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2015, 54: 10299-10302. DOI:10.1002/anie.201502919 |
| [8] | Fischer N, Klapötke T M, Stierstorfer J. 5-Nitriminotetrazole 1-oxide: an exciting oxygen-and nitrogen-rich heterocycle[J]. Eur J Inorg Chem, 2015: 4628-4632. |
| [9] | Dippold A A, Lzsák D, Klapötke T M, et al. Combining the advantages of tetrazoles and 1, 2, 3-triazoles: 4, 5-bis (tetrazole-5-yl)-1, 2, 3-triazole, 4, 5-bis (1-hydroxytetrazol-5-yl)-1, 2, 3-triazole, and their energetic derivatives[J]. Chem Eur J, 2016, 22: 1768-1778. DOI:10.1002/chem.201504624 |
| [10] | Tselinskii I V, Mel'nikova S F, Romanova T V. Synthesis and reactivity of carbohydroximoyl azides: i. aliphatic and aromatic carbohydroximoyl azides and 5-substituted 1-hydroxytetrazoles based thereon[J]. Russian J Organ Chem, 2001, 37(3): 430-436. DOI:10.1023/A:1012453012799 |
| [11] | Fischer N, Klapötke T M, Reymann M, et al. Pushing the limits of energetic materials-the synthesis and characterization of dihydroxylammonium 5, 5'-bistetrazole-1, 1'-diolate[J]. J Mater Chem, 2012, 22: 20418-20422. DOI:10.1039/c2jm33646d |
| [12] | Fischer N, Klapötke T M, Marchner S, et al. A selection of alkali and alkaline earth metas salts of 5, 5'-Bis (1-hydroxytetrazole) in pyrotechnic compositions[J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2013, 38: 448-459. DOI:10.1002/prep.201200177 |
| [13] |
许诚, 毕福强, 张敏, 等. 1, 1'-二羟基-5, 5'-联四唑二羟胺盐及碱金属盐的合成、溶解度测定及关联[J].
含能材料, 2015, 23(3): 208-212. XU Cheng, BI Fu-qiang, ZHANG Min, et al. Synthesis, measurement and correlation of solubility of dihydroxylammonium and alkali metal salts of 5, 5'-bistetrazole-1, 1'-diolate[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials (Hanneng Cailiao), 2015, 23(3): 208-212. |
| [14] | Sheldrick G M. SHELXS-97, Program for solution of crystalstructures[CP], University of Gottingen, Germany, 1990. |
| [15] | Sheldrick G M. SHELXL-97, Program for refinement of crystalstructures[CP], University of Gottingen, Germany, 1997. |
| [16] | LI Fu-gang, BI Yan-gang, ZHANG Tong-lai, et al. Nitrogen-rich salts based on the energetic[monoaquabis (N, N, -bis (1H-tetrazol-5-yl) amine)-zinc (Ⅱ)] anion: a promising design in the development of new energetic materials[J]. Inorg Chem, 2015, 54: 2050-2057. DOI:10.1021/ic503021c |
| [17] | Kissinger H E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis[J]. Anal Chem, 1957, 19: 1702-1706. |
| [18] | Ozawa T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data bull[J]. Chem Soc Jpn, 1965, 38: 1881-1886. DOI:10.1246/bcsj.38.1881 |
| [19] | ZHANG Zhi-bin, XU Cai-xia, ZHANG Jian-guo, et al. Synthesis, crystal structure and properties of a new 1D polymeric nitrogen-Rich energetic complex {TAG[Li (BTO)(H2O)]}n based on 1H, 1'H-5, 5'-bitetrazole-1, 1'-diolate (BTO)[J]. RSC Adv, 2016(6): 73551-73559. |

A new green energetic material dirubidium 5, 5′-bis (tetrazole-1-oxide) (BTORb) was synthesized and characterized.




