2. 山西北方兴安化学工业有限公司, 山西 太原 030051
2. Shanxi NorthernXing'an Chemical Industry Co, Ltd, Taiyuan 030051, China
含能热塑性弹性体(ETPE)作为固体推进剂粘合剂, 可赋予推进剂高能量、钝感、低特征信号和可回收等优点[1-3]。含能热塑性弹性体是指含有硝酸酯基(—ONO2)、硝基(—NO2)、硝胺基(—NNO2)、叠氮基(—N3)、二氟胺基(—NF2)等含能基团的热塑性弹性体[4]。其中叠氮类含能热塑性弹性体具有放热量大、分解时不需要耗氧、与硝胺类炸药具有良好的相容性等优点得到了人们广泛关注, 其中以聚叠氮缩水甘油醚(GAP)基ETPE为代表。GAP基ETPE为软—硬段结构, 软段部分或全部由GAP构成, 赋予ETPE高能量进而提高GAP基ETPE推进剂燃速; 硬段由氨基甲酸酯链段构成, 赋予ETPE高拉伸强度和高弹性模量, 为此基于GAP基ETPE粘合剂的固体推进剂已成为热塑性弹性体推进剂的研究热点[5]。
固体推进剂燃烧性能调节是其应用的关键技术之一, 为使GAP基ETPE推进剂高速、稳定燃烧, 添加燃速催化剂是最简单有效的方法。研究表明燃速催化剂能够有效提高推进剂燃速主要是其对粘合剂和氧化剂的热分解产生正催化作用[6-8]。目前推进剂中主要依据燃速催化剂对不同种类氧化剂热分解影响来选取和使用合适燃速催化剂, 研究表明过渡金属或其氧化物和二茂铁及其衍生物是有效催化高氯酸铵(AP)热分解的燃速催化剂[9-10]; 铅盐(碳酸铅、柠檬酸铅等)是促进硝胺类氧化剂(黑索今(RDX)、奥克托今(HMX)等)热分解有效燃速催化剂; 碳物质与金属类催化剂复合能进一步提高对含有RDX推进剂的催化效果[11]。而不同燃速催化剂对粘合剂热分解影响报道较少, 近年来国内只有王刚[12]研究了不同燃速催化剂对P(BAMO/AMMO)热分解影响。因此研究不同燃速催化剂对GAP基ETPE推进剂主要组分GAP基ETPE热分解影响十分必要。目前对GAP基ETPE推进剂研究主要涉及GAP基ETPE粘合剂的合成、表征和自身热分解性能[13-15]和少量GAP基ETPE模型推进剂热分解报道, Youa等[16]研究了GAP-ETPE/RDX推进剂热分解行为, 表明推进剂在150~250 ℃出现一个热分解阶段, 在转化率α<0.2时推进剂热分解活化能达到170 kJ·mol-1, 推进剂热分解初始阶段为RDX液相分解, ETPE加入对RDX蒸发及气相分解产生限制。综上, 燃速催化剂对GAP基ETPE推进剂常用氧化剂AP、RDX和HMX热分解影响研究有诸多报道, 而有关燃速催化剂对GAP基ETPE本身热分解影响研究未见报道。故选取几种能够有效催化AP和RDX热分解的燃速催化剂, 采用差示扫描量热法(DSC)和热重分析(TG)研究它们对GAP基ETPE粘合剂热分解性能的影响, 为GAP基ETPE在固体推进剂中应用奠定基础。
2 实验部分 2.1 试剂与仪器氧化铜(CuO):化学纯, 天津博迪化工股份有限公司; 三氧化二铁(Fe2O3):化学纯, 天津市登科化学试剂有限公司; 碳黑(CB):化学纯, 宏源化工原料有限公司; 碳酸铅(PbCO3):化学纯, 天津市光复精细化工研究所; 高氯酸铵((NH4)2 Cr2O7):化学纯, 成都格雷西亚化学技术有限公司; 亚铬酸铜(Cr2Cu2O5):化学纯, 营口天元化工研究所股份有限公司; 柠檬酸铅(C6H5O7Pb):化学纯, 营口天元化工研究所股份有限公司; 3-硝基-1, 2, 4-三唑-5-酮(NTO)铅盐(NP):国营245厂; GAP基ETPE粘合剂:实验室自制[15], 相对分子质量31000, GAP基ETPE以70%的GAP为软段, 以30%的HMDI和BDO为硬段, 弹性体中理论—N3含量为29.7%;四氢呋喃(THF):分析纯, 北京市通广精细化工公司。
热失重分析(TG, METTLER TOLEDO TGA/DSC同步热分析仪), 氧化铝坩埚, 试样量小于1 mg, 动态气氛为高纯氮气, 升温速率10 ℃·min-1; 差示扫描量热法(DSC, NETZSCH DSC 204), 氧化铝坩埚, 试样量小于1 mg; 动态气氛为:高纯氮气, 流量为40 mL·min -1; 升温速率10 ℃·min -1。
2.2 样品制备准确称量10 g GAP基ETPE于烧瓶中, 加入100 mL THF, 升温至55 ℃, 磁力搅拌使其完全溶解, 准确称量0.5 g燃速催化剂于烧瓶中, 继续搅拌30 min, 将烧瓶置于超声水浴中分散30 min, 减压蒸馏除去溶剂, 得到ETPE粘合剂与燃速催化剂的混合物, 置于真空干燥箱内, 60 ℃下真空干燥4 h制得样品。
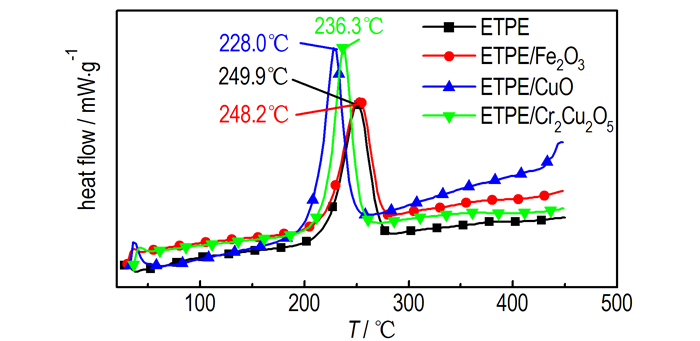
3 结果与讨论 3.1 过渡金属氧化物及其复合金属氧化物对ETPE催化作用Fe2O3、CuO和Cr2Cu2O5催化ETPE热分解的TG-DTG和DSC曲线如图 1、图 2所示, 相关特征量列于表 1。表 1中Ti表示TG曲线起始分解温度, Tp1表示DTG曲线的第一阶段分解峰温, Tp2表示DTG曲线的第二阶段分解峰温, Tp3表示DTG曲线的第三阶段分解峰温, Tp表示DSC曲线热分解放热峰温, ΔH表示叠氮基团分解放热焓, 表 2和表 3同此。
|
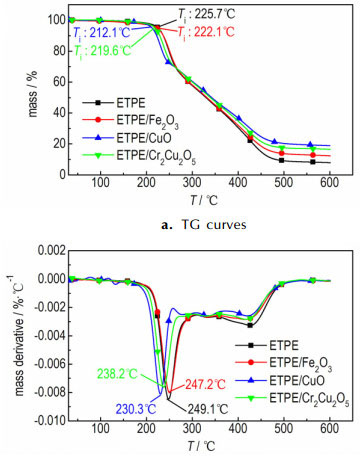
图 1 过渡金属氧化物及复合金属氧化物催化ETPE热分解TG-DTG曲线 Fig.1 TG-DTG curves of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by transition metal oxides and complex metal oxides |
|
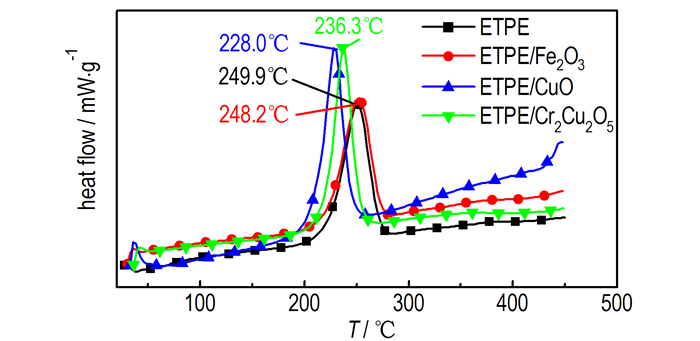
图 2 过渡金属氧化物及复合金属氧化物催化ETPE热分解DSC曲线 Fig.2 DSC curves of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by transition metal oxides and complex metal oxides |
| 表 1 过渡金属氧化物及复合金属氧化物催化ETPE热分解特征量 Tab.1 Characteristic data of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by transition metal oxides and complex metal oxides |
| 表 2 铅盐催化ETPE热分解特征量 Tab.2 Characteristic data of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by lead salts /ETPE |
| 表 3 炭黑催化ETPE热分解特征量 Tab.3 Characteristic data of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by CB |
如图 1所示, ETPE粘合剂的TG曲线出现了三个失重阶段:第一个失重阶段在210~280 ℃, 失重质量分数约31%, 与GAP基ETPE中叠氮基团的质量分数(29.7%)基本一致, 同时表 1中ETPE的DTG曲线中第一阶段分解峰温Tp1与DSC曲线中ETPE热分解放热峰温Tp相对应, 因此第一个失重阶段对应于侧链叠氮基团的热分解过程; 第二个失重阶段出现在280~380 ℃, 对应于HMDI与BDO所构成的氨基甲酸酯链段的分解; 第三个热分解阶段出现在380~490 ℃, 对应于聚醚主链的分解, 与文献报道关于GAP基ETPE热分解性能一致[13, 15]。在DTG曲线中观察到3个分解过程最大失重速率峰分别在249.1, 331.9, 431 ℃。
Fe2O3、CuO和Cr2Cu2O5与ETPE组成的混合样品TG曲线也出现了三个热失重阶段, 失重阶段出现的温度范围与ETPE的热失重曲线类似, 都在210~280 ℃出现第一个失重阶段, 在280~380 ℃出现第二个失重阶段, 在380~490 ℃出现了第三个失重阶段, 由此可以看出, 这三种燃速催化剂加入没有改变ETPE的热分解历程。由TG分析结果可知Fe2O3、CuO、Cr2Cu2O5加入使ETPE起始分解温度分别提前了3.6, 13.6, 6.1 ℃。由表 1可知, Fe2O3、CuO、Cr2Cu2O5使叠氮基团分解峰温分别提前了1.7, 21.9, 13.6 ℃; CuO、Cr2Cu2O5加入使ETPE表观分解热分别增加75.5, 84 J·g-1; Fe2O3加入使ETPE粘合剂表观分解热降低137.9 J·g-1。综合比较认为CuO与Cr2Cu2O5对ETPE粘合剂热分解有较好的催化效果。
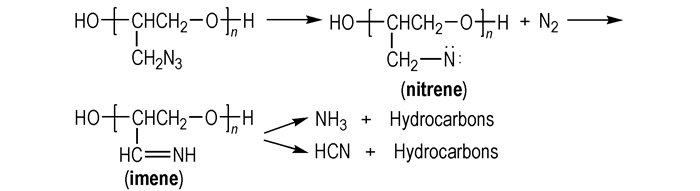
由上述分析可知, 燃速催化剂加入主要对ETPE中叠氮基团的热分解产生影响, 由GAP热分解历程(图 3)可知, 叠氮基团热分解第一步为RN—N2键的断裂生成氮宾(nitrene), 其次氮宾重排生成亚胺(imine), 放出N2, 亚胺(imine)经H转移和自由基转移生成NH3或者C—C键断裂生成HCN等, 其中生成NH3是放热反应, 生成HCN是吸热反应[18]。燃速催化剂催化叠氮基团热分解可能是因叠氮基团易与过渡金属络合[19], CuO与Cr2Cu2O5的活化中心与叠氮基团(—N3)形成活化络合物, 降低反应活化能, 促进了RN-N2键断裂生成氮宾并且释放N2, 使叠氮基团分解峰温提前; 而Fe2O3催化效果不佳可能是Fe和Cu、Cr相比不易与叠氮基团形成活化络合物, 故使叠氮基团分解峰温影响不大; 在后续反应中没有促进亚胺分解, 相当于在粘合剂体系中加入了惰性物质, 故Fe2O3加入使ETPE表观分解热降低。
|
图 3 GAP的热分解历程 Fig.3 Thermal decomposition process of GAP |
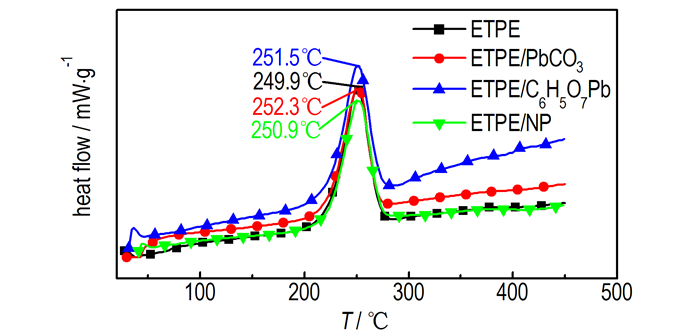
PbCO3、C6H5O7Pb和NP催化ETPE热分解的TG-DTG和DSC测试曲线如图 4和图 5所示, 相关特征量列于表 2。
|
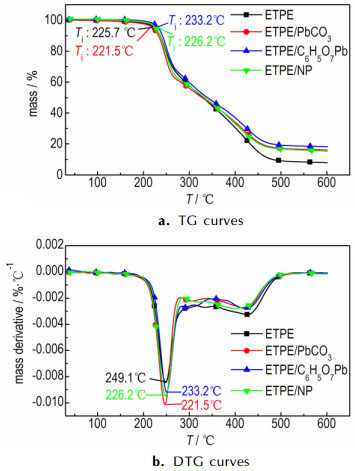
图 4 铅盐催化ETPE热分解TG-DTG曲线 Fig.4 TG-DTG curves of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by lead salts |
|
图 5 铅盐催化ETPE热分解DSC曲线 Fig.5 DSC curves of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by lead salts/ETPE |
由表 2可知, PbCO3、C6H5O7Pb和NP三种燃速催化剂加入同样也没有改变ETPE热分解历程, PbCO3加入使ETPE起始分解温度提前了4.2 ℃, C6H5O7Pb、NP加入使ETPE起始分解温度分别滞后7.5, 0.5 ℃。由表 2可知, PbCO3、C6H5O7Pb、NP使叠氮基团分解峰温分别滞后了2.6, 1.6, 1.0 ℃; PbCO3、NP分别使ETPE表观分解热分别降低58.8, 47.3 J·g-1, C6H5O7Pb使ETPE表观分解热增加43.4 J·g-1。从TG与DSC分析结果综合比较可知, PbCO3、C6H5O7 Pb和NP加入均使ETPE粘合剂叠氮基团分解温度滞后, PbCO3、NP使ETPE表观分解热分别降低58.8 J·g-1和47.3 J·g-1, C6H5O7Pb使ETPE表观分解热增加43.4 J·g-1, 故三种铅盐类燃速催化剂对ETPE催化效果不佳。
铅盐类燃速催化剂催化对ETPE叠氮基团分解峰温影响较小, 可能是铅盐无法和叠氮基团形成活性络合物, 其中C6H5O7Pb和PbCO3、NP相比使ETPE表观分解热增加, 可能是由于C6H5O7Pb能促进亚胺H转移和自由基再结合生成NH3, 生成NH3是放热反应, 故C6H5O7Pb加入使ETPE的表观分解热有升高。
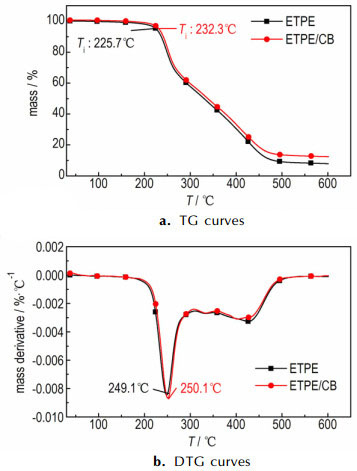
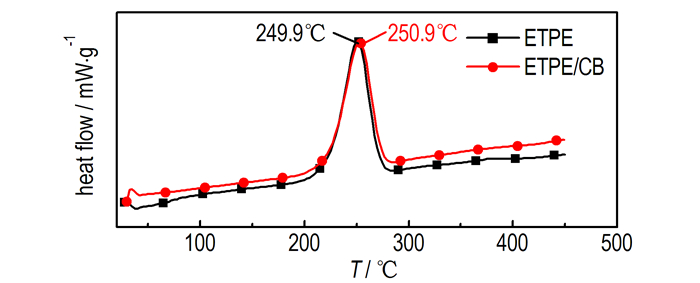
3.3 炭黑对ETPE催化作用CB催化ETPE热分解的TG和DSC曲线如图 6、图 7所示, 相关特征量列于表 3。
|
图 6 炭黑催化ETPE热分解TG-DTG曲线 Fig.6 TG-DTG curves of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by CB |
|
图 7 炭黑催化ETPE热分解DSC曲线 Fig.7 DSC curves of catalyzing the thermal decomposition of ETPE by CB |
由表 3可知, CB与ETPE粘合剂组成的混合样品的TG曲线同样也出现了三个阶段, 失重阶段出现的温度范围与ETPE的热失重曲线类似, CB加入也没有改变ETPE粘合剂的热分解历程。CB加入对ETPE粘合剂起始分解温度滞后6.6 ℃。由表 3可知, CB加入使叠氮基团热分解峰温滞后1.1 ℃; CB加入使ETPE粘合剂表观分解热增加103.1 J·g-1。综合比较可知CB对ETPE起始分解温度与叠氮基团分解峰温影响小, 与前两类燃速催化剂相比使ETPE表观分解热增加较多, CB对ETPE热分解催化效果要略优于铅盐类燃速催化剂和Fe2O3, 而劣与CuO与Cr2Cu2O5。
CB对ETPE热分解影响可能是CB无法和叠氮基团形成活性络合物, 没有促进RN—N2键的断裂, 所以对ETPE叠氮基团分解峰温影响较小, 但CB可以促进亚胺的H转移和自由基再结合生成更多NH3, 使经C—C键断裂吸热生成的HCN量相对减少, 故CB加入使ETPE表观分解热增加。
4 结论分析GAP基ETPE中加入不同的燃速催化剂的TG-DTG结果可知, 几种燃速催化剂加入没有改变GAP基ETPE的热分解历程, 主要对GAP基ETPE中叠氮基团热分解性能产生影响:
(1) 过渡金属氧化物及其复合氧化物类燃速催化剂中, CuO和Cr2Cu2O5使GAP基ETPE叠氮基团分解峰温分别提前21.9 ℃、13.6 ℃, CuO和Cr2Cu2O5使GAP基ETPE表观分解热分别增加75.5,84 J·g-1, Fe2O3使GAP基ETPE叠氮基团分解温度提前1.7 ℃, Fe2O3使GAP基ETPE表观分解热降低137.9 J·g-1。
(2) 铅盐类燃速催化剂中, PbCO3、C6H5O7Pb、NP使叠氮基团分解峰温分别滞后了2.6, 1.6,1.0 ℃, PbCO3、NP使ETPE表观分解热分别降低58.8,47.3 J·g-1, C6H5O7Pb使ETPE表观分解热增加43.4 J·g-1。
(3) CB使GAP基ETPE叠氮基团分解峰温滞后1.1 ℃, 使GAP基ETPE表观分解热增加103.1 J·g-1。
综合比较几种燃速催化剂对GAP基ETPE热分解影响可知, CuO和Cr2Cu2O5是促进GAP基ETPE热分解的最理想的燃速催化剂。
| [1] |
Talawar M B, Sivabalan R, Mukundan T, et al. Environmentally compatible next generation green energetic materials (GEMs)[J].
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161: 589-607. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.011 |
| [2] |
Kawamoto A M, Diniz M F, LourencoV L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of GAP/BAMO copolymers applied at high energetic composite propellants[J].
Aerosp Technol Manage, 2010, 2: 307-322. DOI:10.5028/jatm.2010.02037910 |
| [3] |
罗运军, 王晓青, 葛震.
含能聚合物[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011: 142-150.
LUO Yun-jun, WANG Xiao-qing, GE Zhen. Energetic Polymers[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, Beijing, 2011: 142-150. |
| [4] |
Sikder A K, Reddy S. Review on energetic thermoplastic elastomers(ETPEs) for military science[J].
Propellants, Exploives, Pyrotechnics, 2013, 38: 14-28. DOI:10.1002/prep.v38.1 |
| [5] |
Badgujar D M, Talawar M B, Asthana S N, et al. Advances in science and technology of modern energetic materials: an overview[J].
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 151: 289-305. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.039 |
| [6] |
Mulage K S, Mishra A K. Effect of ballistic modifiers on the burnrate of extruded composite propellant formulations based on thermoplastic binder[J].
International Journal of Energetic Materials and Chemical Propulsion, 2012, 11(4): 375-388. DOI:10.1615/IntJEnergeticMaterialsChemProp.v11.i4 |
| [7] |
Isert S, Groven L J, Lucht P R, et al. The effect of encapsulated nanosized catalysts on the combustion of composite solid propellants[J].
Combustion and Flame, 2014 |
| [8] |
顾健, 吴京汉. 燃速催化剂LBC对GAP推进剂主要组分热分解行为的影响[J].
固体火箭技术, 2011, 34(4): 492-496. GU Jian, WU Jing-han. Effect of lead-salt burning-rate catalyst LBC on thermal decomposition behaviors of key constituents of GAP propellant[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2011, 34: 492-496. |
| [9] |
Kapoor I P S, Srivastava P, Singh G. Nanocrystalline transition metal oxides as catalysts in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J].
Propellants, Exploives, Pyrotechnics, 2009(34): 351-356. |
| [10] |
杨毅, 曹新富, 刘磊力, 等. 纳米过渡金属粉对AP热分解的催化作用[J].
含能材料, 2005, 13(5): 273-277. YANG Yi, CAO Xin-fu, LIU Lei-li, et al. Catalysis of nanometer transition metals on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2005, 13(5): 273-277. |
| [11] |
王雅乐, 卫芝贤, 康丽. 固体推进剂用燃烧催化剂的研究进展[J].
含能材料, 2005, 13(1): 273-277. WANG Ya-le, WEI Zhi-xian, KANG Li. Progress on combustion catalysts of solid propellant[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2005, 13(5): 273-277. |
| [12] |
王刚, 葛震, 罗运军. 几种常用燃速催化剂对P(BAMO /AMMO)含能粘合剂热分解性能的影响[J].
含能材料, 2014, 22(5): 621-645. WANG Gang, GE Zhen, LUO Yun-jun. Effect of several burning rate catalysts on the thermal decomposition properties of P(BAMO /AMMO) energetic binder[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2014, 22(5): 621-645. |
| [13] |
吕勇, 罗云军, 郭凯, 等. GAP型含能热塑性聚氨酯弹性体热分解反应动力学研究[J].
固体火箭技术, 2010, 33(3): 315-318. LV Yong, LUO Yun-jun, GUO Kai, et al. Study on thermal decomposition kinetics of GAP based Energetic thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technolog, 2010, 33(3): 315-318. |
| [14] |
张在娟, 罗运军. 含不同扩链剂的聚叠氮缩水甘油醚基含能热塑性弹性体的合成与力学性能[J].
高分子材料科学与工程, 2014, 30(11): 40-44. ZHANG Zai-Juan, LUO Yun-jun. Synthesis and mechanical properties of glycidyl azide polymer-based energetic thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers with different chain extender[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2014, 30(11): 40-44. |
| [15] |
Zhang Z J, Wang G, Wang Z, et al. Synthesis and characterization of novel energetic thermoplastic elastomers based on glycidyl azide polymer (GAP) with bonding functions[J].
Polym Bull, 2015, 72: 1835-1847. DOI:10.1007/s00289-015-1375-7 |
| [16] |
Youa J S, Kanga S C, Kweon S K, et al. Thermal decomposition kinetics of GAP ETPE/RDX-based solid propellant[J].
Thermochimica Acta, 2012, 537: 51-56. DOI:10.1016/j.tca.2012.02.032 |
| [17] |
You J S, Noh S T. Rheological and thermal properties ofglycidyl azide polyol-based energetic thermolplastic polyurethane elastomers[J].
Polymer International, 2013, 62(2): 158-164. DOI:10.1002/pi.2013.62.issue-2 |
| [18] |
陈智群, 刘艳, 刘子如, 等. GAP热分解动力学和机理研究[J].
固体火箭技术, 2003, 21(4): 52-54. CHEN Zhi-Qun, LIU Yan, LIU Zi-Ru, et al. Research of GAP thermal decomposition kinetics and mechanism[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technolog, 2003, 21(4): 52-54. |
| [19] |
陈沛, 赵凤起, 杨栋, 等. 纳米级金属粉对GAP热分解特性的影响[J].
推进技术, 2000, 21(5): 73-76. CHEN Pei, ZHAO Feng-Qi, YANG Dong, et al. Effect of nanometal powder on thermal decomposition characteristics of glycidyl azide polymer[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2000, 21(5): 73-76. |
To selecte the optimum burning rate catalyst for the thermal decomposition of GAP-based energetic thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer(ETPE), the effect of the burning rate catalysts Fe2O3, CuO, Cr2Cu2O5, PbCO3, C6H5O7Pb, NP and CB on the thermal decomposition properties of GAP-based ETPE were studied by TG and DSC.




