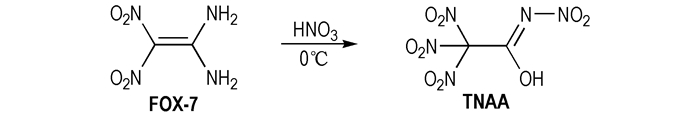
高能氧化剂是固体推进剂、复合火药及混合炸药中的核心组成组分, 不仅是武器火力系统完成弹丸发射、火箭和导弹运载的动力能源, 还是弹药完成终点毁伤的威力能源[1-2]。随着新战争形势的不断发展, 对低污染特征信号氧化剂的需求变得尤为迫切, 自20世纪中期起, 国外专家为无卤氧化剂的研发做出了极大的努力[3]。经过数十年的努力, 许多无卤氧化剂相继问世, 例如二硝基胺羟胺(HADN)、二硝酰胺铵(ADN)和硝仿肼(HNF)等[4-9]。最新研究表明, 具有多硝基乙酰胺酸结构的化合物不仅具有较高的氧平衡和能量密度, 而且分子间可形成氢键网络结构, 因此具有较低的感度[10-11]。美国爱荷华大学的Shreeve等[12]设计合成得到一种具有多硝基乙酰胺酸结构的含能化合物—四硝基乙酰胺酸(TNAA), 其晶体密度为1.84 g·cm-3, 氧平衡(CO2)为30%, 撞击感度为19 J, 理论比冲为209 s, 具有高密度、高氧平衡且不敏感的特点, 是一种潜在的高能氧化剂。
本研究参考并改进文献[12]合成方法, 以1, 1′-二氨基-2, 2′-二硝基乙烯(FOX-7)为原料, 经浓硝酸硝化及有机溶剂萃取等步骤得到目标产物TNAA, 使用1H NMR、13C NMR、IR、MS及元素分析等手段对目标化合物结构进行表征。对比四种有机萃取溶剂所得到的TNAA收率及纯度, 确定二氯甲烷为最佳萃取溶剂。采用热重分析法(TG)和差示扫描量热法(DSC)研究其热行为, 并采用Kissinger[13]和Ozawa[14]方法计算得到TNAA热分解反应的表观活化能(EK和EO)、指前因子(A), 并进一步通过相关热力学方程[15]计算得到TNAA热分解反应的的活化焓(ΔH≠)、活化熵(ΔS≠)和活化吉布斯自由能(ΔG≠)、自加热分解温度(TSADT)以及热爆炸临界温度(Tb)等物化参数[16], 为该化合物下一步应用研究提供参考。
2 实验部分 2.1 试剂与仪器试剂: FOX-7, 西安近代化学研究所自制[17]; 浓硝酸(98%), 分析纯, 树德化工; 二氯甲烷, 分析纯, 西陇化工; 氯仿, 分析纯, 西陇化工; 四氯化碳, 分析纯, 西陇化工; 乙酸乙酯, 分析纯, 西陇化工; 硫酸镁, 分析纯, 西陇化工。
仪器: LC 2010A型高效液相色谱仪(归一化法), 日本岛津公司; NEXUS870型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪, 美国热电尼高力公司; AV 500型(500 MHz)超导核磁共振仪, 瑞士BRUKER公司; 飞行质谱micrOTOF-QⅡ, 德国Bruker公司; VARIO EL 3型元素分析仪, 德国EXEMENTAR公司; TGA/DSC 2 STARe热分析系统, 瑞士Mettler公司。
2.2 实验过程0 ℃条件下, 将1.48 g FOX-7(10 mmol)分批加入10 mL浓硝酸中, 搅拌至完全溶解; 保持在0 ℃条件下继续搅拌2 h后, 将反应液倒入碎冰中, 并用适量二氯甲烷溶剂进行萃取, 再经水洗、硫酸镁干燥后, 减压蒸干溶剂得到目标产物TNAA(2.27 g, 产率为95.0%, 纯度为99.4%), 其合成路线见Scheme 1。
|
Scheme 1 |
1H NMR(CDCl3-d6): δ 8.5457 (s, H); 13C NMR(CDCl3): δ 150.375, 120.733。IR (KBr, ν/cm-1): 3389(s), 3294(s), 2884(w), 1638(vs), 1605(s), 1570(m), 1497(s), 1384(w), 1324(w), 1262(s), 1109(m), 1064(w), 994(w), 907(m), 854(s), 801(s), 774(w), 713(w), 656(w), 502(w)。MS (DEI+): m/z: 238.0 [C2N5O9]+.元素分析(C2HN5O9, %):理论值, C 10.05, H 0.42, N 29.30;实测值, C 10.09, H 0.48, N 30.05。
2.3 热分析对合成的TNAA样品, 分别进行TG和DSC分析。样品量为0.5~1 mg, 样品池为氧化铝制坩埚; Ar为载体, 流速为100 mL·min-1, 升温区间为30~400 ℃, 升温速率分别为2.5, 5, 10, 20 ℃·min-1。
3 结果与讨论 3.1 不同有机萃取溶剂对TNAA纯度的影响Shreeve等[12]报道的TNAA制备过程为:在室温条件下通过浓硝酸硝化FOX-7, 并在真空条件下去除过量的硝酸, 得到无色棒状晶体TNAA。虽然文献报道的收率较高(93%), 但考虑到其后处理过程需要在真空条件下去除过量硝酸, 导致该过程不易控制, 且相当危险。因此选择一种高效安全的后处理方式对TNAA的合成尤为重要。本研究选用安全易操作的有机溶剂萃取代替文献中的后处理方式, 并着重探讨不同的有机萃取溶剂对目标产物TNAA收率及纯度的影响。
本研究选用二氯甲烷、氯仿、四氯化碳和乙酸乙酯四种有机溶剂作为萃取溶剂, 每种溶剂重复三次, 其收率和纯度的平均值见表 1所示。
| 表 1 不同有机萃取溶剂得到的TNAA收率及纯度 Tab.1 The yield and purity of TNAA extracted by different organic solvent |
四种有机萃取溶剂的后处理对比结果表明:采用二氯甲烷作为萃取溶剂效果最佳, 收率为95.0%, 纯度为99.4%, 明显高于其他三种溶剂。
3.2 TNAA的热分解过程升温速率10 K·min-1下, TNAA的TG和DSC曲线如图 1所示。由图 1a中的TG曲线可知, TNAA在30~400 ℃的分析区间仅有一个明显的快速失重阶段, 失重温度范围为83.3~146.3℃, 失重率为87.7%。图 1b中DSC曲线显示在相同的分析温度区间内, 相对应地出现了一个熔化吸热峰和一个分解放热峰, 其中熔化吸热峰的吸热量为61.7 J·g-1, 初始熔化温度为84.8 ℃, 熔化峰值温度为87.8 ℃; 而分解放热峰的放热量为934.8 J·g-1, 初始分解温度为117.7 ℃, 分解峰值温度为131.4 ℃。以上结果表明TNAA的分解热值较高, 熔化峰值温度接近ADN(93.1 ℃)[18], 而分解峰值温度与HNF(135.2 ℃)相当[19]。

|
图 1 TNAA的热行为 Fig.1 The thermal behavior of TNAA |
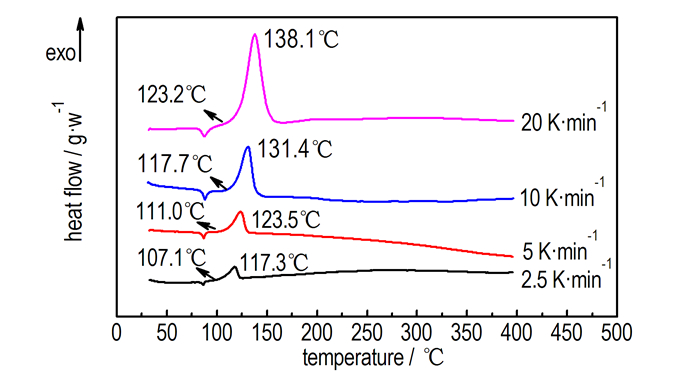
在获得10 K·min-1条件下TNAA热分解过程的基础上, 为进一步对TNAA的非等温热分解动力学参数进行研究, 分别在2.5, 5, 20 K·min-1三个升温速率条件下, 得到三种升温速率条件下的TNAA热分解过程, 2.5, 5, 10, 20 K·min-1四个升温速率条件下TNAA热分解过程对比详见图 2a。根据不同升温速率下的TNAA分解放热峰的峰值温度Tp, 通过Kissinger和Ozawa方程分别进行数据拟合, 拟合趋势线及拟合方程详见图 2b, 根据拟合方程的斜率及截距数值计算得到TNAA的热分解反应活化能E及其指前因子A。Kissinger方程[13]和Ozawa方程[14]如公式(1)、(2)所示。
| $ {\rm{ln}}\frac{\beta }{{T_{\rm{p}}^2}} = {\rm{ln}}\frac{{AR}}{E}-\frac{E}{R}\frac{1}{{{T_{\rm{p}}}}} $ | (1) |
| $ {\rm{log}}\beta + \frac{{0.4567E}}{{R{T_{\rm{p}}}}} = C $ | (2) |

|
图 2 TNAA在不同升温速率条件下的DSC曲线及分解峰温拟合曲线 Fig.2 DSC curves of TNAA at different heating rates and linear fitting curves of decomposition peak temperature |
式中, β为升温速率, K·min-1; E为热分解反应活化能, kJ·mol-1; R为气体常数, 8.314 J·K-1·mol-1; A为指前因子, s-1; Tp为不同升温速率条件下分解放热峰的峰值温度, K; C为常数。计算结果见表 2。
| 表 2 采用Kissinger和Ozawa方法计算得到TNAA的热分解动力学参数a Tab.2 The kinetic parameters of TNAA obtained by Kissinger method and Ozawa methoda |
根据不同升温速率条件下的分解放热峰的初始分解温度Te和峰值温度Tp, 利用公式(3)[20]计算得到升温速率趋向于零时的初始分解温度Te0和峰值温度Tp0, 并进一步通过公式(4)~(8)[21]计算得到TNAA热分解反应的活化焓(ΔH≠)、活化熵(ΔS≠)、活化吉布斯自由能(ΔG≠)、自加速分解温度(TSADT)以及热爆炸临界温度(Tb), 计算结果见表 3。
| $ {T_{(0, {\rm{e, or p}})}} = {T_{(00, {\rm{e0, or p0}})}} + n{\beta _i} + m\beta _i^2\;\;\;\;i = 1 \sim 4 $ | (3) |
| $ \Delta {H^ \ne } = {E_{\rm{K}}}-R{T_{{\rm{p0}}}} $ | (4) |
| $ {A_{\rm{K}}} = \frac{{{k_{\rm{B}}}{T_{{\rm{p}}0}}}}{h}{\rm{exp}}\left( {\frac{{\Delta {S^ \ne }}}{R}} \right) $ | (5) |
| $ \Delta {G^ \ne } = \Delta {H^ \ne }-{T_{{\rm{p0}}}}\Delta {S^ \ne } $ | (6) |
| $ {T_{{\rm{SADT}}}} = {T_{{\rm{p0}}}} $ | (7) |
| $ {T_{\rm{b}}} = \frac{{{E_{\rm{O}}}-\sqrt {E_{\rm{O}}^{^2}-4{E_{\rm{O}}}R{T_{{\rm{e0}}}}} }}{{2R}} $ | (8) |
| 表 3 TNAA的热力学参数 Tab.3 The Thermodynamic parameters of TNAA |
式中, kB为Boltzmann常数, 1.3807×10-23 J·K-1; h为Planck常数, 6.626×10-34 J·s-1。
由表 3可知, TNAA的Te0、Tb及TSADT分别为375.4 K (102.3 ℃)、385.3 K(112.2 ℃)和375.4 K(102.3 ℃), Tb及TSADT与HNF(400.28 K, 395.10 K[19])水平相当。另外, TNAA的ΔH≠、ΔS≠及ΔG≠均为正值, 表明其热分解为放热增熵反应。
4 结论(1) 以FOX-7为原料, 经HNO3硝化及有机溶剂萃取等步骤得到目标产物TNAA, 并通过对比四种有机萃取溶剂对TNAA收率及纯度的影响, 确定二氯甲烷为最佳萃取溶剂, 收率为95.0%, 纯度为99.1%。
(2) 升温速率为10 K·min-1条件的DSC曲线表明TNAA的初始熔化温度为84.8 ℃, 熔化峰值温度为87.8 ℃, 熔化吸热峰的吸热量为61.7 J·g-1; 初始分解温度为117.7 ℃, 分解峰值温度为131.4 ℃, 分解放热峰的放热量为934.8 J·g-1。升温速率趋向于零时的TNAA初始分解温度Te0以及自加速分解温度TSADT均为102.3 ℃, 热爆炸临界温度Tb为112.2 ℃, 表明TNAA的热稳定性与ADN及HNF相当。
(3) 计算得到TNAA的热分解反应活化能E为124.8 kJ·mol-1, 指前因子A为1016.1 s-1。TNAA热分解反应的热力学参数ΔH≠、ΔS≠、ΔG≠分别为121.5 kJ·mol-1, 61.2 J·K-1·mol-1, 98.0 kJ·mol-1, 表明其热分解为放热增熵反应。
| [1] |
Lan Y, Jin M, Luo Y. Preparation and characterization of graphene aerogel/Fe2O3/ammonium perchlorate nanostructured energetic composite[J].
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2015, 74(1): 161-167. DOI:10.1007/s10971-014-3590-3 |
| [2] |
Dey A, Athar J, Varma P, et al. Graphene-iron oxide nanocomposite (GINC): an efficient catalyst for ammonium perchlorate (AP) decomposition and burn rate enhancer for AP based composite propellant[J].
RSC Advances, 2015, 5(3): 1950-1960. DOI:10.1039/C4RA10812D |
| [3] |
Patiño R, Wainscott M R, Cruz-Li E I, et al. Effects of ammonium perchlorate on the reproductive performance and thyroid follicle histology of zebrafish[J].
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2003, 22(5): 1115-1121. DOI:10.1002/etc.v22:5 |
| [4] |
Mandal A K, Kunjir G M, Singh J, et al. Optimization of ammonium sulfamate nitration for the preparation of ammonium dinitramide[J].
Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 2014, 11(1): 83-97. |
| [5] |
Zhang X, Gong X. Theoretical studies on the structures, intra-and inter-molecular hydrogen bonding interactions in HNF and HNF-H2O clusters in the gaseous, aqueous and solid phases[J].
Molecular Simulation, 2015, 41(18): 1528-1539. DOI:10.1080/08927022.2014.999237 |
| [6] |
王婧娜, 张皋, 严蕊, 等. 动态法研究ADN的吸湿性能[J].
含能材料, 2012, 20(1): 86-89. WANG Jing-na, ZHANG Gao, YAN Rui, et al. Hygroscopicity of ADN with dynamic method[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2012, 20(1): 86-89. |
| [7] |
居学海, 肖继军, 肖鹤鸣. 硝仿肼离子对相互作用的密度泛函理论研究[J].
高等学校化学学报, 2003, 24(6): 1067-1071. JU Xue-hai, XIAO Ji-jun, XIAO He-ming. DFT study of the intermolecular interaction of hydrazinium nitroformate ion pair[J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(6): 1067-1071. |
| [8] |
丁黎, 陆殿林. 硝仿肼及其推进剂的研究进展[J].
火炸药学报, 2003, 26(3): 35-38. DING Li, LU Dian-lin. Advance in hydrazinium nitroformate(HNF) and HNF based propellant[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2003, 26(3): 35-38. |
| [9] |
马跃, 张海林. 二硝酰胺铵(ADN)球形化工艺研究[J].
固体火箭技术, 2002, 25(2): 59-62. MA Yue, ZHANG Hai-lin. Study on prilling process of ammonium dinitramide(ADN)[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2002, 25(2): 59-62. |
| [10] |
Axthammer Q J, Krumm B, Klapötke T M. Synthesis of energetic nitrocarbamates from polynitroalcohols and their Potential as high energetic oxidizers[J].
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2015, 80(12): 6329-6335. DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.5b00655 |
| [11] |
Vo T T, Parrish D A, Shreeve J N M. 1, 1-Diamino-2, 2-dintroethene (FOX-7) in copper and nickel diamine complexes and copper FOX-7[J].
Inorganic Chemistry, 2012, 51(3): 1963-1968. DOI:10.1021/ic202288t |
| [12] |
Vo T T, Parrish D A, Shreeve J N M. Tetranitroacetimidic acid: A high oxygen oxidizer and potential replacement for ammonium perchlorate[J].
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(34): 11934-11937. DOI:10.1021/ja5074036 |
| [13] |
Kissinger H E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis[J].
Analytical Chemistry, 1957, 29(11): 1702-1706. DOI:10.1021/ac60131a045 |
| [14] |
Ozawa T. Initial kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric rate and conversion data[J].
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 1965, 38(11): 1881-1886. DOI:10.1246/bcsj.38.1881 |
| [15] |
胡荣祖, 史启祯.
热分析动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 290-295.
HU Rong-zu, SHI Qi-zhen. Thermal Analysis Kinetics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 290-295. |
| [16] |
崔可建, 徐志斌, 王鹏, 等. TNAE的合成和热分解动力学[J].
火炸药学报, 2014, 37(1): 17-20. CUI Ke-jian, XU Zhi-bin, WANG Peng, et al. Synthesis and thermal decomposition kinetics of TNAE[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2014, 37(1): 17-20. |
| [17] |
周诚, 朱勇, 王伯周, 等. FOX-7合成过程中硝化反应的热危险性[J].
含能材料, 2014, 22(01): 53-56. ZHOU Cheng, ZHU Rong, WANG Bo-zhou, et al. Thermal hazards of nitration reaction in the synthesis of FOX-7[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2014, 22(01): 53-56. |
| [18] |
王晓红, 张皋, 赵凤起, 等. DSC/TG-FTIR-MS联用技术研究ADN热分解动力学和机理[J].
固体火箭技术, 2010, 33(5): 554-559. WANG Xiao-hong, ZHANG Gao, ZHAO Feng-qi, et al. Research on the kinetics and mechanism of the thermal decomposition of ADN via DSC/TG-MS-FTIR[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2010, 33(5): 554-559. |
| [19] |
孙笑, 王娟, 周新利. HNF的热分解动力学和热安全性[J].
含能材料, 2014, 22(06): 774-779. SUN Xao, WANG Juan, ZHOU Xin-li. Thermal decomposition kinetics and thermal safety of HNF[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials(Hanneng Cailiao), 2014, 22(06): 774-779. |
| [20] |
CUI K, MENG Z, XU Z, et al. Characterization of hydrazinium 3, 5-Dinitroamine-1, 2, 4-triazole[J].
Journal of Energetic Materials, 2014, 32(1): 60-70. DOI:10.1080/07370652.2012.758190 |
| [21] |
Wang Y, Xu K, Zhao F, et al. Synthesis, crystal structure, and thermal behaviors of 3-Nitro-1, 5-bis (4, 4′-dimethylazide)-1, 2, 3-triazolyl-3-azapentane (NDTAP)[J].
Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2013, 38(5) |
A high oxygen-containing oxidizer(ΩCO2=30%), tetranitroacetimidic acid(TNAA), was synthesized by the nitration reaction of 1, 1′-diamino-2, 2′-nitroethylene(FOX-7) and the organic solvent extraction. The kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of thermal decomposition reaction of TNAA were calculated.




